Unlocking the Secrets of Exoplanet Atmospheres with Quantum Technology
2025-09-05
Author: Rajesh
Revolutionizing Exoplanet Research
For decades, scientists have relied on complex models to analyze the atmospheres of distant exoplanets, meticulously adjusting countless chemical and physical parameters to predict their spectral signatures.
The Challenge of High-Dimensional Data
However, the intricate web of parameters often leads to overwhelming computational demands, slowing down the pace of discovery in this exciting field.
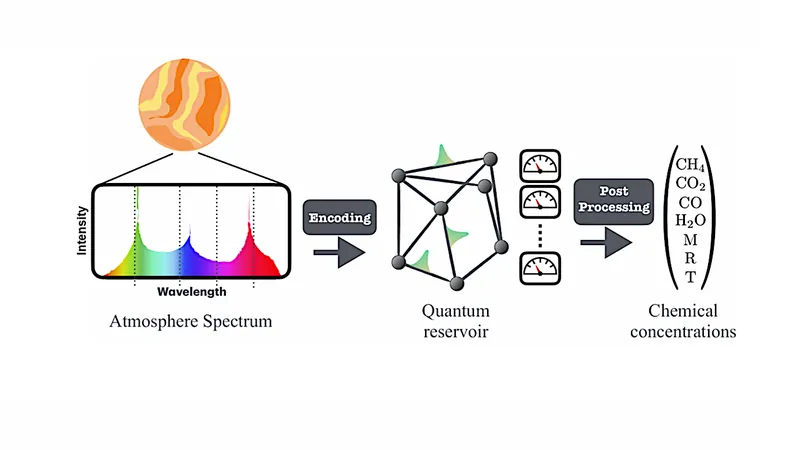
Introducing Quantum Extreme Learning Machines (QELMs)
Enter Quantum Extreme Learning Machines—a cutting-edge approach that harnesses the power of quantum computing to streamline atmospheric retrieval. These innovative algorithms process input data through quantum systems, effectively acting like a black box that enhances efficiency.
A Fault-Tolerant Framework for Atmospheric Retrieval
In a groundbreaking study, researchers have developed a robust framework for extracting vital atmospheric features from exoplanets using QELMs. This method is designed to be fault-tolerant, making it ideal for the limited capabilities of near-term quantum devices. The proof-of-concept was successfully executed on the IBM Fez quantum processor.
The Future of Astrophysics and Quantum Computing
The QELM architecture not only showcases the transformative potential of quantum computing in astrophysical data analysis but also heralds a new era where rapid, precise models revolutionize our understanding of alien worlds. With advancements in this field, we are on the brink of unlocking unprecedented insights into the atmospheres of distant planets.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)