Unlocking the Secrets of Bathyarchaeia: How Marine Microbes Transform Carbon into Unique Lipids
2025-09-19
Author: Daniel
In the depths of our oceans, a fascinating group of microorganisms known as Bathyarchaeia is revolutionizing our understanding of carbon metabolism. Recent research reveals that these unique archaea are exceptionally skilled at assimilating both organic and inorganic carbon, leading to the production of unconventional membrane lipids that set them apart in the microbial world.
Bathyarchaeia: The Unsung Heroes of Marine Ecosystems
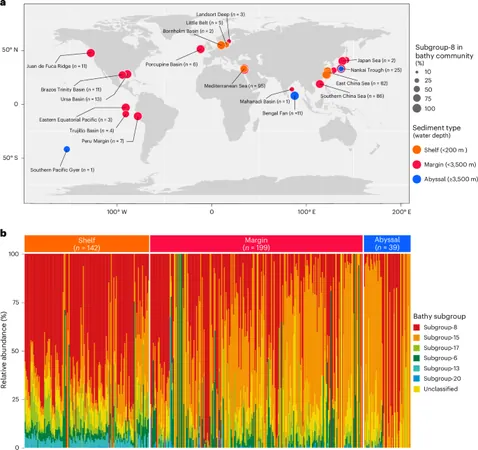
Bathyarchaeia, a dominant subgroup of marine archaea, play a crucial role in our planet's carbon cycle. These microorganisms thrive in anoxic environments, where they have been found to metabolize a wide array of carbon sources—from lignin to methane. Their ability to utilize diverse substrates highlights their metabolic versatility and ecological significance in marine sediments.
Revolutionary Findings in Carbon Assimilation
A groundbreaking study has recently showcased how Bathyarchaeia incorporate different carbon sources into unique lipid structures, specifically butanetriol and pentanetriol. These unconventional lipids not only serve as important biomarkers for studying ancient environmental conditions but also provide insights into the survival strategies of these archaea under extreme conditions.
The Implications of Bathyarchaeia's Lipid Production
The findings surrounding Bathyarchaeia's lipid biosynthesis have far-reaching implications. With their distinct lipid profiles, these microorganisms can reveal changes in environmental conditions over time, potentially informing us about past climate events. Moreover, their efficient carbon assimilation processes might inspire novel biotechnological applications, including bioenergy production.
Future Research Directions
As scientists delve deeper into the ecology and biochemistry of Bathyarchaeia, the potential for discovering new metabolic pathways and interactions within the marine ecosystem becomes increasingly plausible. Understanding these microorganisms could lead to breakthroughs in fields such as environmental science, biotechnology, and climate change mitigation, forging a path toward sustainable solutions for our planet's future.
The remarkable ability of Bathyarchaeia to transform carbon into unique lipids underscores the complexity and dynamism of marine microbial communities. As research continues, we edge closer to unlocking the full potential of these fascinating organisms.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)