Unlocking the Secrets of Alzheimer's: How RTP801 Protein Might Be the Key to Cognitive Decline
2025-05-26
Author: Nur
New Research Sheds Light on Alzheimer's Mechanisms
Innovative findings from the University of Barcelona's Institute of Neurosciences (UBneuro) reveal how a protein known as RTP801 could play a pivotal role in the cognitive decline experienced by Alzheimer's disease patients, the leading cause of dementia. This groundbreaking study utilizes animal models to dive deep into the cellular mechanisms at play and sheds light on potential new therapeutic avenues.
The Role of RTP801 in Astrocytes
According to the research, published in the journal 'Alzheimer's & Dementia', RTP801—a protein linked to the DDIT4 gene—has been identified as a game-changer in the realm of astrocytes, brain cells crucial for maintaining brain health. Previously seen as mere support structures, astrocytes are now recognized as active regulators in neurodegenerative conditions, influencing neuroinflammation, synaptic balance, and overall brain condition.
A Closer Look at Alzheimer's Disease
As we know, Alzheimer's is characterized by harmful accumulations of beta-amyloid plaques outside neurons and tangled tau proteins inside them. This research highlights how RTP801 exacerbates neuroinflammation and neurotoxicity, ultimately propelling the disease forward. The insights gathered could redefine our approach to Alzheimer's management.
Silencing RTP801: A Promising Strategy
Using advanced gene therapy techniques, the research team led by Almudena Chicote examined the effects of reducing RTP801 expression in astrocytes of the hippocampus. The results showed improvements in vital aspects like spatial memory and the functioning of critical parvalbumin-positive (PV+) interneurons, which play a significant role in maintaining the brain's excitatory-inhibitory balance.
Impact on Brain Function and Connectivity
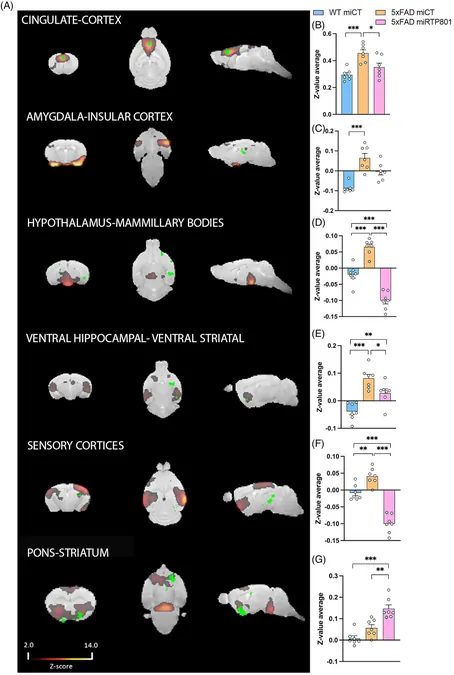
The study revealed that lowering RTP801 levels in astrocytes reduced the hyperconnectivity seen in brain networks of Alzheimer's models. By normalizing RTP801 expression, researchers suggest there could be a restoration of brain connectivity levels akin to those in healthy individuals, potentially halting cognitive decline.
Restoring Balance with GABA
The findings also indicate a decrease in GABA, a critical inhibitory neurotransmitter, in Alzheimer's-affected brains. Remarkably, this reduction can be counteracted by silencing RTP801 in astrocytes, which could help revive GABA production and bolster overall cognitive function.
Future Directions in Alzheimer's Research
This trailblazing research not only identifies RTP801 as an important player in the progression of Alzheimer's disease but also sets the stage for further studies aimed at validating RTP801 silencing as a potential therapeutic strategy. As scientists continue to unravel the complexities of this debilitating disease, hope rises for new interventions that could significantly improve the quality of life for millions.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)