Unlocking the Secrets of Alien Life: How Molecular Assembly and Machine Learning Could Transform Space Exploration
2025-08-04
Author: Wei
Imagine a future where we can spot life on distant planets without making assumptions based on Earth’s biology! New research is suggesting that molecular assembly might just hold the key for such groundbreaking discoveries.
In upcoming Solar System missions, mass spectrometers will play a pivotal role in identifying potential biosignatures. But here’s the catch: we need a way to predict molecular assembly from mass spectrometry data that doesn’t rely on understanding unknown structures. The ultimate goal? An unbiased identification of life forms.
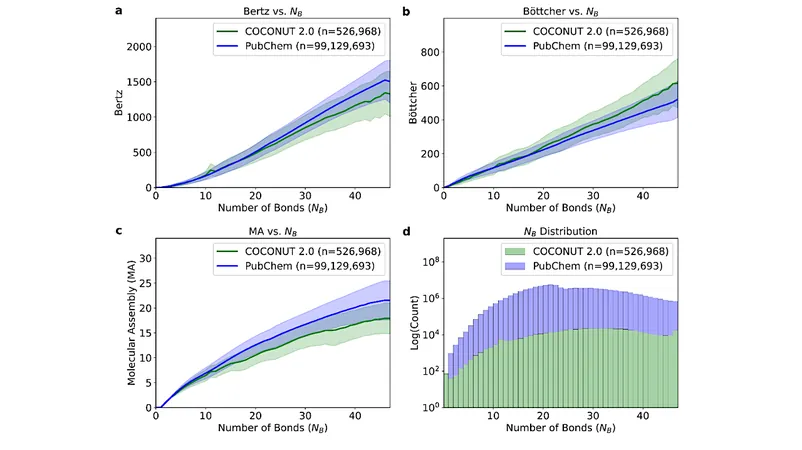
Researchers propose that molecular assembly can meet this challenge. Unlike methods that overlook the history of molecule creation, this innovative approach focuses on how molecules bond together as foundational building blocks. This makes it an interpretable method for detecting life signs.
What’s more, this detection can occur without needing to fully decipher complex molecular structures! Through mass spectrometry, scientists can physically measure these assemblies—something that sets this method apart from traditional complexity measures based on molecular structure.
However, space missions come with their unique constraints. To tackle potential inaccuracies, researchers have developed a cutting-edge machine learning model that predicts molecular assembly with remarkable precision, slashing error rates by threefold compared to earlier models.
But beware: even minor instrumental inconsistencies can double the model’s error rate, underlining the urgent need for standardization in mass spectrometry. These findings reveal a promising avenue: with the creation of standardized mass spectrometry databases, we could achieve accurate predictions of molecular assembly—paving the way for future astrobiology explorations.
Imagine upcoming missions gathering samples from other worlds and using this technology to predict molecular assembly scores directly from their mass spectrometry data—no complex structural analysis required! The RecursiveMA algorithm could also aid space missions that utilize advanced MSn techniques.
With these advancements, we stand on the brink of a new era in astrobiology, potentially revolutionizing how we search for life beyond our planet.




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)