Unlocking the Secrets of Acute Gallstone Pancreatitis: How Biliopancreatic Tree Anatomy Plays a Key Role
2025-04-18
Author: Wei Ling
Understanding Acute Pancreatitis and Its Common Culprit
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is no small matter; it's a serious condition that often stems from gallstones, which are the leading cause worldwide. Researchers have been keen to explore how variations in the anatomy of the biliopancreatic tree—including the gallbladder, cystic duct, common bile duct, and main pancreatic duct—contribute to the onset of this distressing disorder.
The Study: A Deep Dive into Patient Data
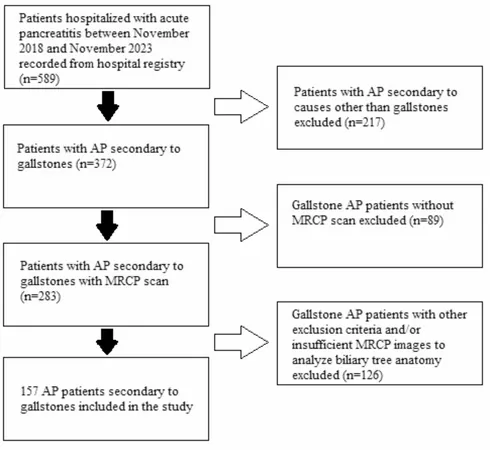
In a groundbreaking study involving 157 patients with gallstone-related AP and a control group of 75, researchers meticulously analyzed MRCP scans to dissect the anatomy at play. They focused on the cystic duct's entry point into the common bile duct, examining whether it opened in a parallel or perpendicular manner, and recorded the diameters of critical ducts along with their angles.
Statistical Goldmine: What the Results Revealed
The findings were nothing short of enlightening. Significant statistical differences emerged in almost all measured parameters, except for the cystic duct opening angle. The acute pancreatitis group showed a tendency for parallel and tortuous cystic ducts, often opening in the second or third part of the common bile duct. Conversely, controls more commonly exhibited acute opening angles and straighter duct courses.
Conclusion: Anatomy Matters in the World of Pancreatitis
The anatomy of the biliopancreatic tree is intricately linked to the development of acute gallstone pancreatitis. While multiple mechanisms might be at work here, this study underscores the pressing need for future research to unpack these connections. With acute pancreatitis on the rise globally, understanding these anatomical variances could prove crucial in identifying at-risk patients and tailoring preventive strategies.
Research Context and Relevance
This study was conducted at Antalya Training and Research Hospital, spanning from 2018 to 2024. The comprehensive approach, including exclusions of confounding factors, ensured a clear focus on gallstone-related cases and set the stage for pivotal insights into acute pancreatitis mechanisms.
Future Directions: The Path Forward
As acute pancreatitis continues to burden healthcare systems, especially considering its potential to escalate to organ failure, ongoing exploration into biliary anatomy and its physiological implications is essential. The study members are advocating for dynamic imaging studies to reveal how anatomical variations might hinder bile and pancreatic fluid flow, thus leading to pancreatitis.
A Potential New Frontier in Pancreatitis Research
This pioneering investigation into the biliopancreatic tree's anatomical variations signifies an important step forward. With anatomical idiosyncrasies potentially leading to increased gallstone formation, the insights gleaned may influence future protocols for monitoring, prevention, and treatment of acute pancreatitis, marking a leap toward better patient outcomes.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)