Unlocking the Secret: Glutamine's Critical Role in Red Blood Cell Development and Its Implications for Disease Treatment
2024-11-15
Author: John Tan
Introduction
Researchers at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital have unveiled a groundbreaking discovery in the world of hematology: the amino acid glutamine plays a pivotal role in the development of red blood cells and may hold the key to treating prevalent blood disorders like sickle cell disease and β-thalassemia.
Understanding Metabolic Processes
As blood stem cells progress through their maturation stages to become fully functional red blood cells, they undergo a series of intricate metabolic processes. Unfortunately, these processes can often go awry in various blood disorders, highlighting the urgency to understand their underlying biology.
Research Findings
In a study published in Science, scientists Jian Xu, Ph.D., and Min Ni, Ph.D., have exposed the significant impact of glutamine metabolism, proposing it as a novel therapeutic target. Their research indicates that not only is modulating glutamine levels a potential treatment strategy, but its concentration may also serve as a biomarker to assess treatment effectiveness.
Unique Characteristics of Red Blood Cells
Astonishingly, red blood cells, which make up a staggering 84% of adult blood cells, do not possess organelles like mitochondria commonly found in other cell types. This unique characteristic prompts important questions about how they meet their metabolic demands while facilitating the synthesis of hemoglobin, the protein responsible for oxygen transport.
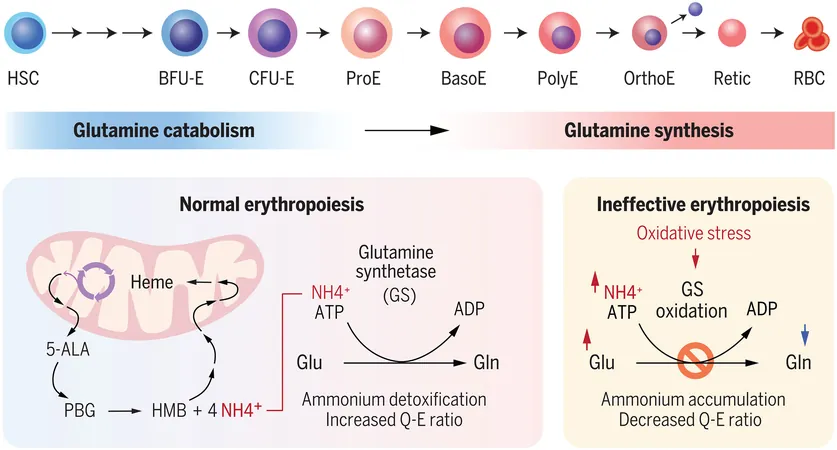
Metabolic Transitions in Red Blood Cell Maturation
The research team systematically characterized metabolic transitions throughout red blood cell maturation. They were surprised to discover a reversal in the use of glutamine during this process. While early maturation stages involve breaking down glutamine for energy, later stages see a shift where cells begin synthesizing glutamine, thanks to the enzyme glutamine synthetase. This enzyme also plays a crucial role in detoxifying ammonium, a waste product of heme production, thus preventing oxidative stress which can hinder red blood cell function.
Implications for Treatment
This groundbreaking revelation has significant implications for treating red blood cell disorders. Current therapeutic drugs for β-thalassemia have been associated with improved cell maturation; however, the mechanisms behind these benefits have remained unclear. The researchers found that the activity of glutamine synthetase is impaired in these disorders, resulting in increased levels of glutamate and ammonia, while glutamine levels dwindle.
Oxidative Stress and Metabolic Deficiency
Interestingly, the team has pinpointed oxidation of glutamine synthetase as a leading cause of this metabolic deficiency in β-thalassemia. In experimental settings, enhancing the expression of this enzyme restored its function, paving potential pathways for effective treatments.
Current Therapeutic Options
Current therapies, such as the drug luspatercept, have shown promise in treating anemia, but their exact modes of action are still under investigation. The researchers identified that luspatercept treatment increased the glutamine-to-glutamate ratio, suggesting a possible link between the drug's effectiveness and the restoration of glutamine levels.
Potential of L-Glutamine Supplements
Additionally, L-glutamine supplements, used to alleviate symptoms of sickle cell disease, might operate similarly by rectifying glutamine synthetase disruptions, offering hope for more effective treatment strategies.
Broader Implications of Research
Beyond implications for red blood cell disorders, this research underscores the potential for using metabolic markers like the glutamine-to-glutamate ratio in diagnosing and tracking various diseases, solidifying glutamine’s significance in medical science.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
As further studies are executed, the findings could not only refine our understanding of red blood cell metabolism but also transform therapeutic approaches for blood disorders, providing millions with renewed hope in their fight against these life-altering conditions.
Stay tuned as we continue to explore the astonishing relationship between metabolic health and blood cell function – you won’t want to miss what we uncover next!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)