Unlocking the Mystery of the Mpemba Effect: A New Scientific Breakthrough
2025-03-19
Author: Rajesh
The Mpemba Effect Explained
The Mpemba effect, a fascinating phenomenon that sparks curiosity and debate, describes how certain substances, like water, may cool down faster when they are hot compared to when they are at a lower temperature. This counterintuitive behavior has captivated scientists for decades but remains a significant puzzle within the realm of theoretical physics.
Challenges in Understanding the Effect
Despite its intriguing nature, the Mpemba effect has not yet been thoroughly explained, primarily due to the limitations of conventional physics in accurately quantifying the speeds at which systems relax to equilibrium. This has led to inconsistencies in experimental observations, as different methods for measuring "relaxation speed" can yield conflicting results.
Breakthrough Research from Kyoto University
A research team from Kyoto University has heralded a breakthrough with the introduction of a novel and unified approach grounded in thermomajorization theory. Published in *Physical Review Letters*, their work provides a rigorous criterion for quantifying the Mpemba effect without the reliance on a specific distance measure—an approach that has plagued preceding scientific literature with ambiguity.
Significance of the Findings
Tan Van Vu, a key researcher, highlighted the significance of their work: "The Mpemba effect has intrigued scientists for years, yet our understanding has been hampered by the variability in how we measure relaxation speed. Our method simplifies this by allowing for a comprehensive analysis that doesn't depend on a single measure.”
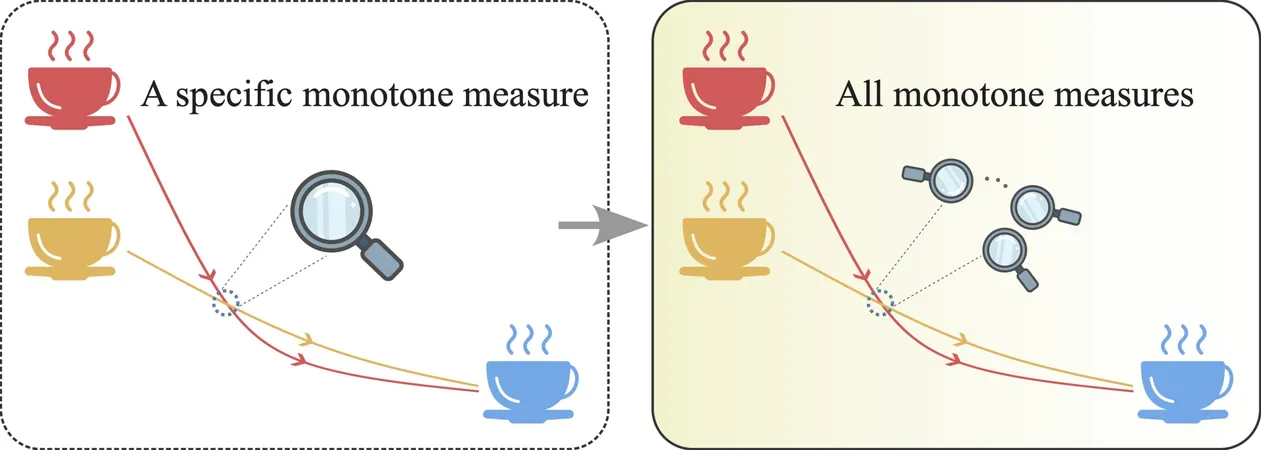
Introducing Thermomajorization Mpemba Effect
This innovative approach, termed the thermomajorization Mpemba effect, effectively rectifies previous inconsistencies. By evaluating all possible monotone distance measures—those that do not increase over time—the researchers established a consistent framework to determine when the Mpemba effect occurs within finite time. Consequently, this methodology can now apply to any classical Markovian stochastic processes.
Broader Implications
Vu elaborated on the broader implications of their findings: "Thermomajorization theory, prominent in statistical physics and quantum thermodynamics, allows us to assess whether hotter systems reach equilibrium faster than cooler ones independently of any particular distance measure." This generality suggests that the Mpemba effect is not constrained to specific temperatures, hinting at its potential ubiquity across various thermal systems.
Practical Applications
The ramifications of this study extend beyond theoretical realms, with implications for practical technology. Vu indicated that understanding thermal relaxation more comprehensively could lead to significant advancements in diverse fields, from optimizing heat engines and refrigeration technologies to enhancing quantum computing processes where quick state initialization is critical.
Future Research Directions
While the team's current focus revolves around classical stochastic processes, their framework is poised to adapt to various systems in future research. They aim to explore open quantum systems governed by quantum master equations, which could eventually unveil new dimensions of the Mpemba effect.
Conclusion and Future Questions
As they look ahead, fascinating questions remain: What is the minimum timescale for the thermomajorization Mpemba effect? Investigating the speed limits of this effect may unlock even deeper insights into the fundamental physical principles at play.
The Ongoing Journey in Thermodynamics
For anyone seeking to delve into the mesmerizing world of thermodynamics, the continued exploration of the Mpemba effect promises to illuminate not just theoretical physics but also practical applications that follow from a deeper understanding of thermal dynamics. Stay tuned; the journey into these scientific mysteries is just beginning!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)