Unlocking the Moon's Secrets: Groundbreaking Study Reveals Minerals from the Far Side
2025-07-14
Author: Daniel
A Historic Leap in Lunar Science
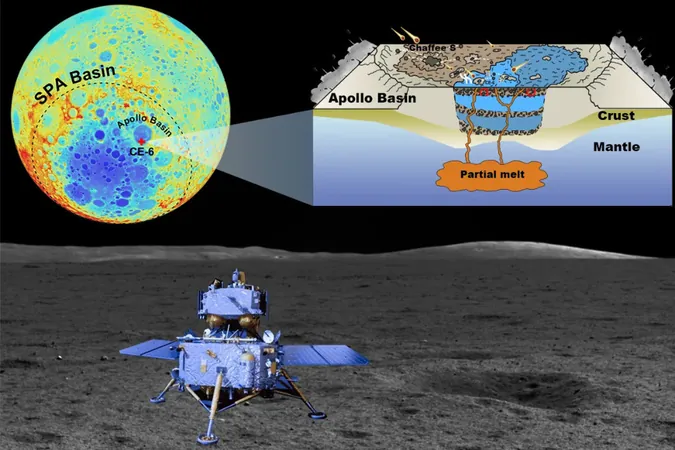
In an unprecedented achievement, Shandong University has unveiled the first-ever mineralogical ground truth report focusing on magnesium-rich pyroxene from the far side of the moon. This groundbreaking research, based on samples brought back by China’s Chang'e 6 mission, illuminates the enigmatic South Pole-Aitken Basin, recognized as the moon's largest, deepest, and oldest crater.
Discoveries That Change Our Understanding
Published in the prestigious journal Communications Earth & Environment, the study signifies a monumental moment in planetary science history. According to Cao Haijun, the lead author and a researcher at Shandong University's School of Space Science and Physics, this endeavor is akin to performing a "deep X-ray scan" of the moon, allowing scientists to reveal the intricate details hidden within its surface.
Revealing the Moon's Hidden Composition
For the first time ever, researchers have accessed high-precision ground truth data, shedding light on unknown aspects of the far side’s geological composition. Cao emphasized the importance of this research, stating, "This data unveils details previously obscured by relying solely on remote sensing techniques. We’ve managed to decode the mineral composition of the SPA Basin’s magnesium-pyroxene annulus using advanced Raman spectroscopic techniques on the lunar soil collected by Chang'e 6."
Implications for Lunar Research
Covering nearly one-eighth of the moon's surface, the SPA Basin holds clues to the moon's formation and evolution. The study revealed a significant presence of low-calcium pyroxene, a mineral rich in magnesium, challenging existing notions about the lunar far side. Cao remarked that these findings could offer fresh perspectives on the origins of SPA's mafic anomalies and the evolutionary history of far side mare soils. This research paves the way for a deeper understanding of not only the moon but also the broader dynamics of our solar system.




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)