Unlocking the Earth's Secrets: How Copper Giants are Formed
2025-07-03
Author: Sarah
A Geological Breakthrough that Could Transform Copper Mining
In a groundbreaking international study, scientists have unveiled the intriguing process behind the formation of the Earth's most substantial copper deposits—an essential element for advancing clean energy technologies and vital infrastructure.
The Secrets of Southern Tibet's Riches
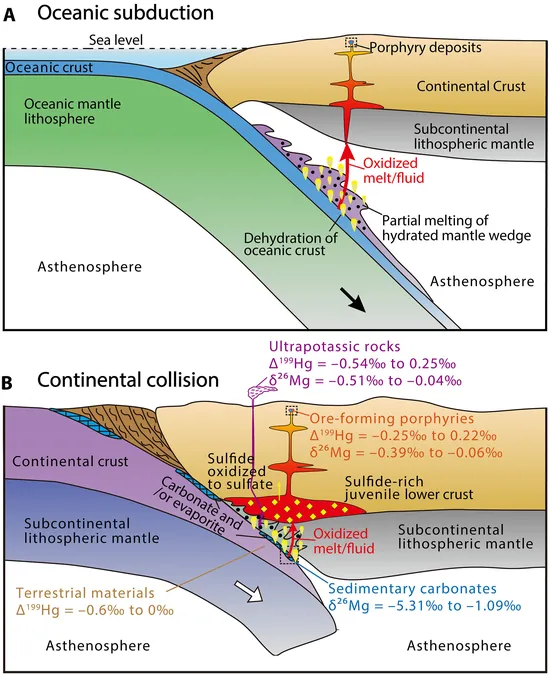
Led by Dr. Yongjun Lu from The University of Western Australia, the research focuses on the Gangdese belt in southern Tibet, a hotspot for porphyry copper deposits. These precious deposits are known as the biggest global source of copper, typically forming when hot hydrothermal fluids penetrate fractured rocks, precipitating copper minerals.
The Puzzle of Post-Subduction Copper
What’s baffling scientists is that many significant copper deposits, like those in southern Tibet, emerged millions of years after the subduction process halted. This long-standing mystery has finally been cracked.
Recycled Material: Nature’s Copper Catalyst
The research team discovered that sediments from the Indian plate—rich in oxidized materials such as carbonates and sulfates—were recycled deep into the mantle during continental collisions. This recycled material was vital in generating oxidized magmas, which are key in concentrating copper.
A Game-Changer for Exploration
Using innovative techniques like mercury and magnesium isotope analyses, the scientists found compelling evidence that oxidized sedimentary materials significantly contributed to post-collisional magmas. Dr. Lu explained, "Think of it as a second wind for copper-forming magmas. Even when the oceanic plate is no longer present, recycled crustal sediments can still power metal-rich systems for eons."
Shifting Paradigms in Copper Resource Exploration
These groundbreaking findings could redefine exploration strategies for copper, encouraging prospectors to target tectonic regions that were previously neglectually overlooked. Dr. Lu emphasizes the importance of potential post-subduction environments, especially where continental collisions occur, as promising frontiers for future exploration.
In High Demand: The Global Copper Conundrum
The timing of this research couldn’t be more critical. With the rapid global shift towards renewable energy and electrified economies, the demand for copper is soaring. This study not only sheds light on the origins of our natural resources but also opens new avenues for sustainable excavation.
Collaborative Efforts Bring New Insights
The research was a collaborative effort involving esteemed partners from institutions across China and Europe, illustrating the global importance of understanding our Earth's geological treasures.
 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)