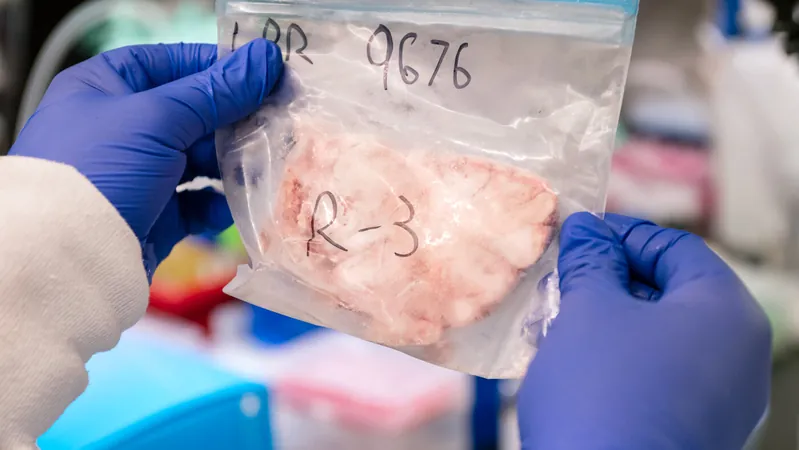

Unlocking the Brain's Secrets: How Guardian Cells Influence Alzheimer's and Stroke Risks!
2025-07-28
Author: Rajesh
The Hidden Guardians of Brain Health
When it comes to brain health, neurons often steal the spotlight. However, a complex web of blood vessels and immune cells tirelessly works as the brain's protectors, controlling what enters, sweeping away waste, and forming the vital blood-brain barrier.
Shocking New Research Sheds Light on Genetic Risks
A groundbreaking study by Gladstone Institutes and UC San Francisco has unveiled that several genetic risk factors for debilitating conditions like Alzheimer's and stroke may actually impact these very guardian cells. Senior researcher Dr. Andrew C. Yang stresses the importance of studying these border cells, suggesting they might be pivotal in diseases such as Alzheimer's.
The Mystery of 'Junk DNA' Unraveled
For years, large-scale studies linked numerous DNA variants to increased risks of neurological diseases. However, a perplexing mystery remained: over 90% of these variants are located outside of genes—previously dismissed as "junk DNA." Until now, scientists lacked a complete understanding of where these genetic switches operate within the brain's diverse cell types.
Revolutionary Technology Changes the Game
To tackle this challenge, the Gladstone team developed MultiVINE-seq, a cutting-edge technology that isolates vascular and immune cells from postmortem brain tissue. This innovative method allowed researchers to map gene activity and their regulatory mechanisms within each cell, revealing crucial insights into how genetic risks operate.
Distinct Pathways for Different Diseases
Surprisingly, the researchers found that genetic variations affect the brain's barrier system in dramatically different ways depending on the disease. For instance, variants associated with stroke weakened the structural integrity of blood vessels, while those linked to Alzheimer's heightened immune responses, leading to excessive inflammation.
Uncovering the Role of T Cells in Alzheimer’s Risk
Among the findings, a particular variant near the PTK2B gene stood out, especially active in T cells—immune cells crucial to brain health. This genetic variant appears to supercharge T cells, conducting them into the brain where they may contribute to the toxic environment associated with Alzheimer's.
A New Hope for Therapeutics
Excitingly, PTK2B is already recognized as a 'druggable' target, with therapies in clinical trials for cancer. This new discovery opens up a tantalizing possibility for repurposing these drugs to combat Alzheimer’s disease!
New Horizons for Brain Protection
This research not only highlights the significance of vascular and immune cells in the brain but also paves the way for innovative therapeutic approaches. These guardian cells live at the intersection of brain health and external environment, making them ideal candidates for novel treatments that enhance brain defenses from the outside.
As Dr. Yang notes, by focusing on these actually lying at the barrier between the brain and the body, we may unlock new pathways for lifestyle changes and drug targets that can fundamentally change how we protect against neurological diseases.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)