Unlocking Mental Health: A Deep Dive into Older Adults’ Awareness and Access to Mental Health Services in China
2025-05-15
Author: Ming
A Growing Concern: Mental Health Among China's Aging Population
As China faces an accelerating rate of population aging, the prevalence of mental disorders among older adults is alarming. With mental health issues becoming increasingly common in this demographic, enhancing mental health literacy (MHL) is key. High levels of MHL can significantly aid in early identification of mental disorders, combat stigma, and facilitate better access to timely support and treatment.
The Challenge of Mental Health Services Access
Despite the potential benefits, mental health literacy among older Chinese residents remains dismally low, with a meta-analysis revealing that only 28.12% demonstrate adequate knowledge of mental health. Research indicates that older adults in China are often reluctant to seek mental health services (MHS) due to self-stigma, leading to a general aversion towards recognizing their need for help.
What Influences Mental Health Literacy?
Factors such as stigma, family support, and worries over medication side effects profoundly influence MHL and accessibility to MHS among older adults. Individual characteristics like gender, age, education, psychological conditions, and cognitive function have shown significant correlations with MHL and help-seeking behaviors.
Community Engagement: A Pathway to Better Mental Health Awareness
Community-based services are gaining traction in China as a response to the needs of older adults, yet their utilization remains low. Studies suggest that regular participation in community activities positively impacts health literacy and overall mental well-being, though its effectiveness in promoting MHL and service demand remains an open question.
Living Alone: A Double-Edged Sword
With an increasing number of older adults living alone, the impact on their mental health is concerning. While isolation can motivate some to seek knowledge about mental health, it may also hinder cognitive function and reduce their openness to new information and services.
Bridging Research Gaps to Promote Better Outcomes
There remains a clear need for targeted research focusing on the factors affecting MHL and service access among older adults. Notably, the dynamics differ significantly based on cultural context, and understanding community engagement’s role could lead to tailored interventions.
Study Overview: Methodology and Key Findings
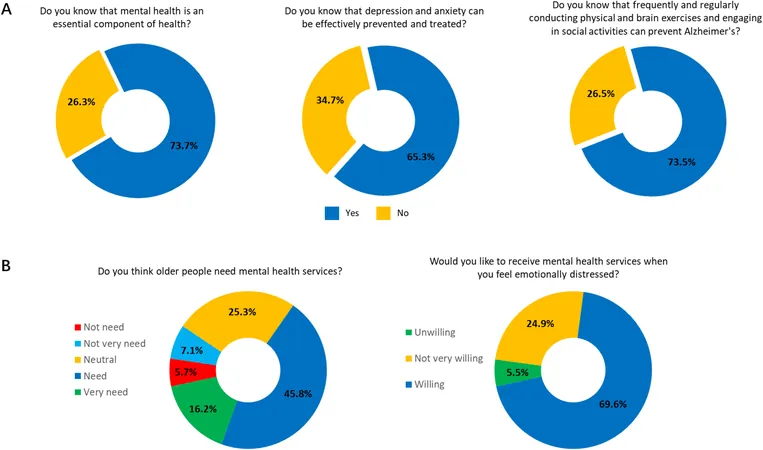
A recent study involving 494 older adults across Guangzhou examined MHL and service demand. It highlighted that frequent community participation correlated with significantly better awareness of mental health issues and an increased likelihood of service demand. Strikingly, 62% of participants expressed demand for MHS, with 70% willing to utilize such services if emotionally distressed.
Conclusion: A Call for Action
This study sheds light on the pressing mental health needs of older adults in China, calling for further exploration of effective strategies that link community engagement with enhanced mental health literacy. Creating awareness and improving accessibility to mental health services for older adults is urgently needed to foster healthier aging in China.
Future Directions: Addressing the Unique Needs of Isolated Seniors
As mental health continues to be an overlooked issue among older individuals, developing targeted interventions for seniors living alone should be prioritized. By identifying specific barriers related to their circumstances, healthcare providers can better serve this vulnerable population and promote positive mental health outcomes.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)