Unlocking Insights: A Groundbreaking MRI Dataset for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Segmentation
2025-08-20
Author: Li
A Global Cancer Crisis
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is not just another cancer; it ranks as the sixth most common globally and is especially rampant in Southeast Asia, where incidence rates can soar to 7.7 per 100,000 for men. What makes NPC so insidious? Factors such as Epstein-Barr virus infections, genetics, and environmental triggers play a crucial role. Alarmingly, the likelihood of men developing NPC is three times higher than that of women, peaking between the ages of 40 and 60.
Survival Rates and Treatment Challenges
The five-year survival rates for NPC are a mixed bag, ranging from 60% to a hopeful 90%, but not without complications—14% face local recurrence, and 21% may develop distant metastases. Radiotherapy stands as the frontline treatment for early-stage tumors. For more advanced cases, doctors often combine induction chemotherapy with concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT), emphasizing the importance of precise tumor mapping through advanced imaging.
MRI: The Gold Standard for NPC Assessment
When it comes to assessing NPC, MRI reigns supreme. Unlike CT scans, MRI showcases superior soft tissue contrast and eliminates exposure to ionizing radiation. While CT is adept at imaging bone structures, MRI offers multi-modal imaging capabilities and high-resolution perspectives in all three planes—axial, coronal, and sagittal. This level of detail allows for accurate staging, essential for planning effective treatment.
The Need for Advanced Imaging Techniques
Despite the advantages, manual tumor delineation remains a hurdle, requiring substantial expert input. This is where machine learning and advanced algorithms like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) step in. By employing automatic segmentation techniques, researchers strive to enhance the accuracy of tumor identification while minimizing human error.
Introducing a Revolutionary Dataset
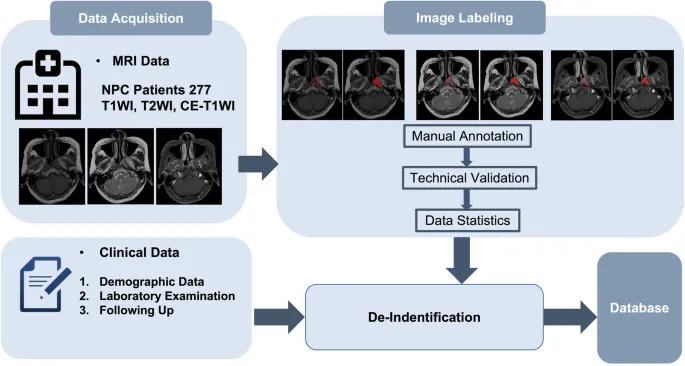
Excitingly, our study unveils a robust dataset comprising MRI scans from 277 patients diagnosed with NPC at The First People’s Hospital of Foshan in China. This treasure trove of data includes detailed histopathological confirmations, imaging sequences, and long-term monitoring of patients, paving the way for future innovations in NPC treatment.
Meticulous Data Collection Process
To ensure the highest quality, all included patients had no prior treatment history that might distort tumor morphology. Each MRI session adhered to rigorous standardization protocols, employing six different MRI machines calibrated to maintain consistent image quality across multiple sequences—T1-weighted, T2-weighted, and contrast-enhanced images.
Streamlined Annotation and Segmentation
The manual segmentation process involved a detailed review by experienced radiologists, ensuring tumor borders were accurately identified. This meticulous approach yields a binary mask for each scan, effectively identifying tumor presence in each pixel—an invaluable resource for AI model training and validation.
Harnessing the Power of Collaboration
Public sharing of our meticulously curated dataset signifies a critical advance in NPC research. By opening access to high-quality annotated data, researchers worldwide can collaborate more effectively, replicate important findings, and accelerate breakthroughs in automated segmentation technologies that could revolutionize how NPC is diagnosed and treated.
Ethics and Integrity in Research
All research activities were conducted following ethical guidelines approved by the relevant committees, ensuring the confidentiality of patient data while paving the way for innovative research that could save lives.
Join the NPC Revolution!
This groundbreaking dataset not only brings hope for more reliable NPC assessments but also represents a significant leap forward in leveraging machine learning for medical imaging. As the battle against NPC continues, this collaborative endeavor aims to transform how healthcare professionals diagnose and treat one of the world's most critical cancers.




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)