Unlocking Human Brain Secrets: The Role of a Unique DNA Enhancer in Cortical Development
2025-05-20
Author: Mei
Revolutionary Discovery in Brain Genetics
A groundbreaking study led by Duke University Medical Center has unveiled a human-specific DNA enhancer, known as HARE5, that plays a pivotal role in regulating the growth of neural progenitor cells and the overall size of the cerebral cortex. This enhancer has the potential to reshape our understanding of developmental pathways that influence brain size and neuron count.
Why This Matters: The Human Advantage
Compared to other species, humans boast a remarkably larger and complex cerebral cortex, which is essential for our advanced cognitive abilities. Researchers have long been tracking Human Accelerated Regions (HARs)—segments of our DNA that have evolved uniquely in humans and are now linked to genes crucial for brain development and differentiation.
The HARE5 Breakthrough
Targeting HARE5, located on chromosome 10, scientists found that it enhances the expression of the FZD8 gene, crucial to the WNT signaling pathway, influencing cortical development. Despite its significance, the exact mechanisms by which human-specific genetic variations in HARE5 affect neural progenitor behavior were yet to be fully understood.
Innovative Research Techniques
In their study titled "A human-specific enhancer fine-tunes radial glia potency and corticogenesis", researchers employed advanced genome-editing techniques to investigate HARE5’s impact on cortical development. They created mouse models featuring edited versions of HARE5 from humans, chimpanzees, and mice, and analyzed neural progenitor cells and cortical organoids for enhancer activity and proliferation.
Surprising Findings
The results revealed that human HARE5 knock-in mice exhibited a notable increase in both cortical size and neuron numbers, especially in the upper layers. Enhanced proliferation and self-renewal of radial glial cells were observed during the early developmental stages, pointing to a significant neurogenic potential.
Genetic Variations at Play
Four specific nucleotide changes in HARE5 drove increased activity of the enhancer, with two main variants contributing most significantly. Alarmingly, mutations associated with autism spectrum disorder near one of these variants were shown to reduce enhancer activity, illustrating a potential genetic link to decreased neural progenitor proliferation.
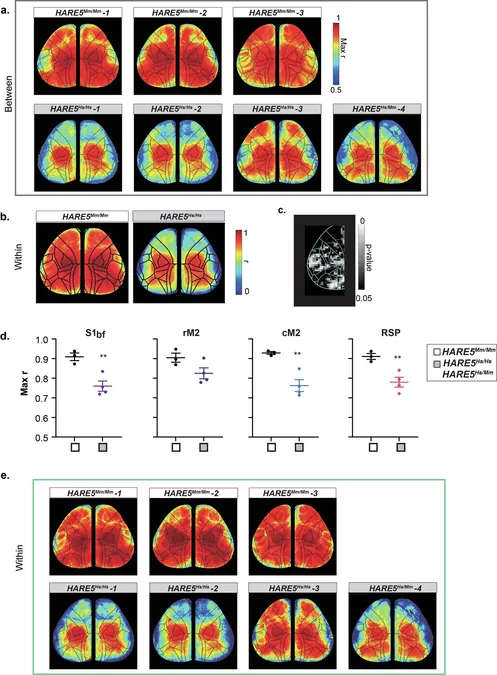
Broader Implications for Brain Structure
The study also revealed increased functional independence between different cortical regions in HARE5 knock-in mice. This suggests that small genetic tweaks can have profound effects on brain network dynamics and cognitive function.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Neurodevelopment Research
The discoveries regarding HARE5 provide a crucial framework for understanding how genetic variations influence brain complexity and neurodevelopmental disorders. Future research will delve deeper into similar DNA sequences to unlock further secrets about neural function and how they relate to cognitive development, particularly concerning conditions like autism spectrum disorder.
In Summary: A Leap Toward Understanding Human Evolution
This significant research highlights how minute alterations in our DNA can mold the architecture of our brains, driving home the intricate relationship between genetics and cognition. As we uncover more about these enhancers, we edge closer to explaining the enigmatic evolution of the human brain.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)