Unlocking Heart Health: How Psychosocial Factors Can Supercharge Lifestyle Interventions
2025-08-30
Author: Daniel
The Vital Role of Psychosocial Factors in Heart Health
Recent research has shed light on the crucial impact of psychosocial factors in lifestyle interventions aimed at preventing cardiovascular disease (CVD). A scoping review examined the interplay between individual mental states and lifestyle changes, revealing how personality traits, emotions, mental health, and social support can significantly alter intervention outcomes.
What’s Inside the Review?
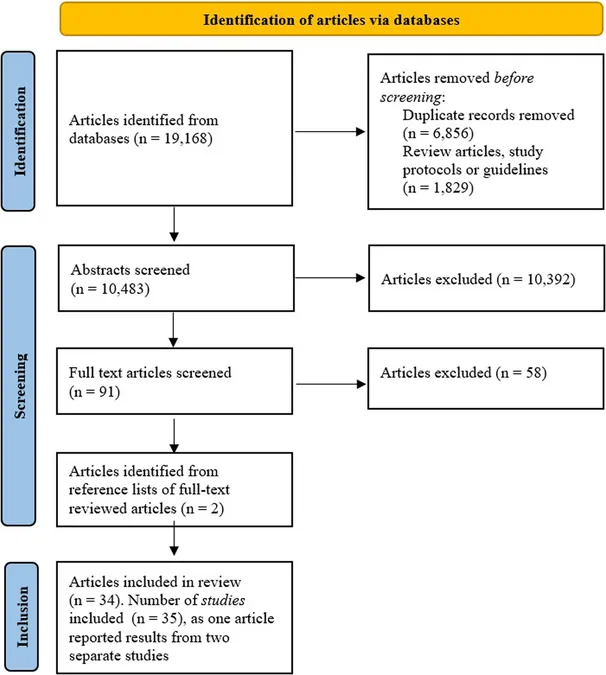
Conducted with meticulous detail, this review analyzed 35 studies published between 2000 and 2025. It utilized the PRISMA-ScR guidelines, focusing on adults aged 18 and older without pre-existing cardiovascular conditions. Researchers combed through esteemed databases, including PubMed and Scopus, to identify relevant empirical studies that specifically highlighted psychosocial moderators.
The Power of Personality and Emotional Factors in Lifestyle Changes
The findings from this extensive review illustrate an intriguing picture. Approximately 77% of these studies found that psychosocial factors modulated the effectiveness of lifestyle interventions. Notably, emotional stability and personality traits such as optimism and conscientiousness emerged as pivotal players in successful lifestyle adjustments. For instance, individuals characterized by higher self-efficacy and motivation generally exhibited greater benefits from lifestyle interventions.
Social Support: The Unsung Hero of Behavioral Change
One particularly enlightening aspect of the review is the substantial role of social support in lifestyle modification. Seven out of eight studies validated its importance, suggesting that robust social networks can significantly amplify the effectiveness of health interventions. Whether it's through encouragement or simply companionship, social aspects play a vital role in facilitating adherence to health objectives.
Mental Health: A Double-Edged Sword
On the downside, the review exposed a troubling trend—poor mental health consistently correlated with diminished intervention successes. Participants grappling with anxiety and depression showed reduced responsiveness to lifestyle changes. This highlights an essential area for future interventions, indicating that mental health support should be integrated into physical health programs for optimal results.
Cognitive Factors: The Hidden Drivers
Cognitive factors like health literacy also rose to prominence in this review. Notably, individuals with better cognitive skills demonstrated greater responsiveness to interventions, underscoring the need for tailored health education that fosters an understanding of health risks and lifestyle changes.
Spanning a Diverse Landscape of Interventions
This review covered a wide array of interventions—from dietary adjustments to physical activity programs and smoking cessation efforts. Nevertheless, it also revealed a significant gap in research targeting younger adults and underrepresented populations. Moreover, the intervention designs often lacked uniform measurement tools, making it challenging to draw definitive conclusions.
What’s Next? Your Health Depends on It!
As cardiovascular diseases continue to be a leading health concern globally, understanding the psychosocial dimensions of health interventions is more critical than ever. This review not only opens a dialogue about incorporating psychological considerations into physical health strategies but also calls for a new wave of research focused on diverse and younger populations.
Takeaway: Individualized Approaches are Key
Ultimately, to optimize heart health interventions, clinicians and researchers must take into account the psychosocial landscape of their patients. Tailoring interventions to address mental health, social support, and cognitive beliefs can propel more individuals towards sustainable lifestyle changes that safeguard against cardiovascular disease.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)