Unlocking Heart Health: How Inflammatory Markers Predict CHD Risk for NAFLD Patients!
2025-07-03
Author: Li
Understanding the Link Between NAFLD and CHD
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) are two major health issues that share common pathways, including inflammation and insulin resistance. Despite this connection, the precise role of inflammation in elevating CHD risk within NAFLD patients has been largely unexplored. This study aims to bridge that knowledge gap by evaluating ten immunoinflammatory indexes as predictive tools for CHD among individuals suffering from NAFLD.
Methods: A Comprehensive Analysis of NAFLD Patients
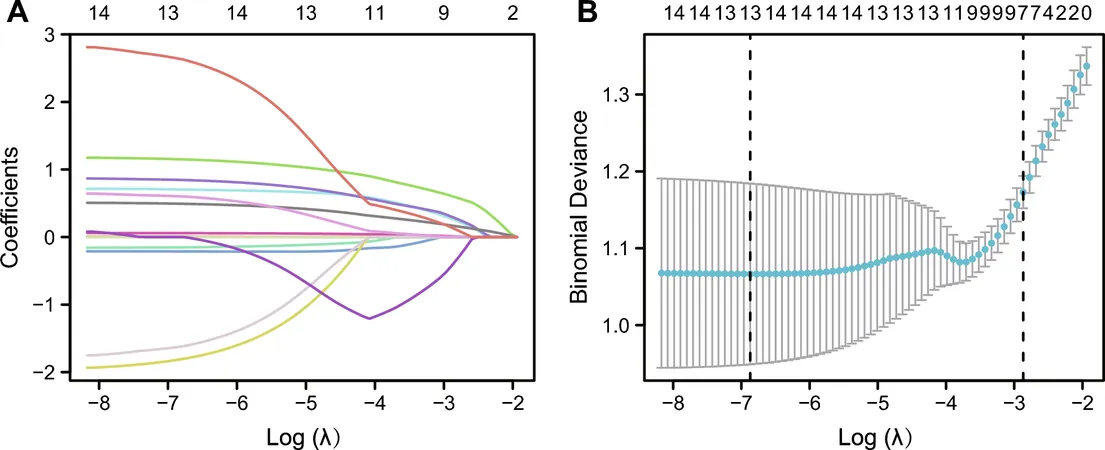
In this study, we analyzed data from 407 NAFLD patients who underwent coronary angiography, classifying them into two groups: those with both NAFLD and CHD (250 patients) and those with NAFLD only (157 patients). Various statistical methods—including Lasso regression and logistic regression—were employed to identify independent risk factors and ascertain the predictive power of inflammatory markers concerning CHD.
Findings: Key Predictors Revealed!
Among the patient cohort, half exhibited both NAFLD and CHD. After thoroughly adjusting for factors like age, sex, and smoking history, the Neutrophil-to-HDL Ratio (NHR) emerged as the most significant risk factor for CHD in NAFLD patients. Other inflammatory markers such as NLR, SII, and SIRI were also associated with increased risk. Remarkably, PNR was identified as a protective factor against CHD.
The Power of Machine Learning in Predicting Risk
Using three sophisticated machine learning algorithms—Random Forest (RF), Support Vector Machine (SVM), and Generalized Linear Model (GLM)—the study pinpointed key inflammatory predictors of CHD. The Random Forest model stood out for its accuracy in forecasting outcomes. The SHAP method was applied to elucidate the contributions of each feature, leading to the creation of a refined diagnostic nomogram capable of predicting CHD risk in NAFLD patients.
Conclusion: A New Era in Risk Assessment!
The findings underscore the critical role of inflammatory markers in assessing CHD risk among NAFLD patients. In particular, the NHR index proves to be a powerful predictive tool for healthcare professionals aiming to identify high-risk individuals. This innovative study paves the way for better risk stratification strategies and personalized treatment plans to combat CHD within this vulnerable population.
Implications for Future Research
As heart disease continues to be a leading health concern globally, this research emphasizes the urgency of tackling underlying conditions like NAFLD. Yet, further studies are needed to validate these findings across diverse populations and refine prediction models to enhance clinical decision-making.





 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)