Unlocking Health Savings: How Internet Use Can Lower Healthcare Costs for China’s Aging Population
2025-05-28
Author: Rajesh
The Rising Tide of Healthcare Costs in China
As China confronts a demographic shift with an aging population experiencing chronic diseases, the financial burden of healthcare has reached alarming levels. Over 66% of older adults grapple with chronic conditions, leading to skyrocketing healthcare expenses that threaten the country’s economic stability.
The Internet: A Double-Edged Sword for Health Costs
While the internet has become a vital lifeline for health management, its impact on healthcare spending remains largely uncharted territory for middle-aged and older adults. This study dives deep into the correlation between internet usage and healthcare expenditures among individuals aged 45 and above with chronic diseases.
Study Insights: Data and Methods
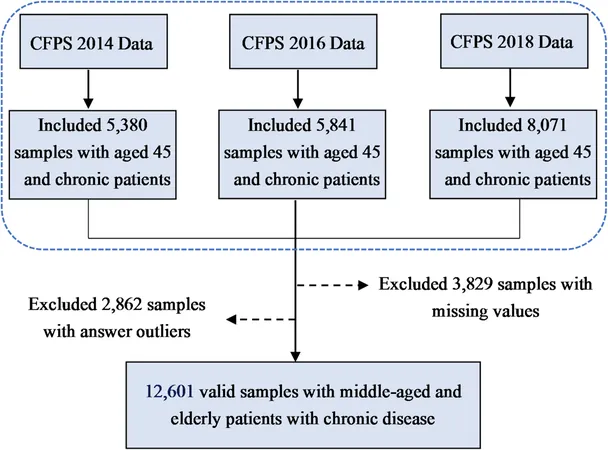
Using the Chinese Family Panel Survey (CFPS) data from 2014 to 2018, researchers focused on a sample of over 12,000 respondents aged 45 and up with chronic illnesses. Employing various statistical methods, including fixed effects models and instrumental variables, the study examines the multifaceted relationship between internet use, self-rated health, and healthcare costs.
Astounding Findings: Internet Usage Reduces Healthcare Burden
Results reveal that internet usage is significantly linked to lower healthcare expenses. Specifically, those who used the internet reported a reduction in overall costs, while self-rated health emerged as a crucial mediator, accounting for over 30% of the effect. However, the nuances of these findings indicate that while internet use lowers outpatient costs, it correlates with higher hospitalization expenses, especially in rural areas.
Urban vs. Rural: A Tale of Two Worlds
Interestingly, the study uncovered a stark urban-rural divide. Internet usage led to reduced costs for urban patients but increased hospital expenditures for rural individuals. This disparity raises critical questions about access to quality online health information and the implications of digital literacy on health outcomes.
The Path Forward: Bridging the Digital Divide
These findings spotlight the pressing need to enhance internet access and digital literacy among older adults, particularly in rural regions. By empowering the aging population to effectively harness online health resources, China can alleviate the financial strain of chronic disease management and promote better health outcomes.
Conclusion: Internet as a Tool for Health Empowerment
In conclusion, this study highlights the internet's potential as a transformative tool for reducing healthcare expenditure among middle-aged and older adults with chronic diseases, particularly through improved self-rated health. As China grapples with rising healthcare costs, prioritizing internet access and education could pave the way for a healthier, more economically stable future.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)