Unlocking Health Insights: The Surprising Link Between TyG-WHtR Index and Cardiometabolic Multimorbidity in China's Aging Population
2025-09-02
Author: Arjun
A Growing Global Concern: Cardiometabolic Multimorbidity
As the world faces escalating health challenges, cardiometabolic multimorbidity (CMM) stands out as a significant threat, particularly among middle-aged and older adults. Defined by the simultaneous presence of multiple cardiometabolic diseases—such as heart disease, diabetes, and strokes—CMM is becoming increasingly prevalent, especially in China where rates soar between 5.94% and 16.9%. This concerning trend emphasizes the urgent need for effective risk assessment methods.
Innovative Index: Triglyceride-Glucose-Waist Height Ratio
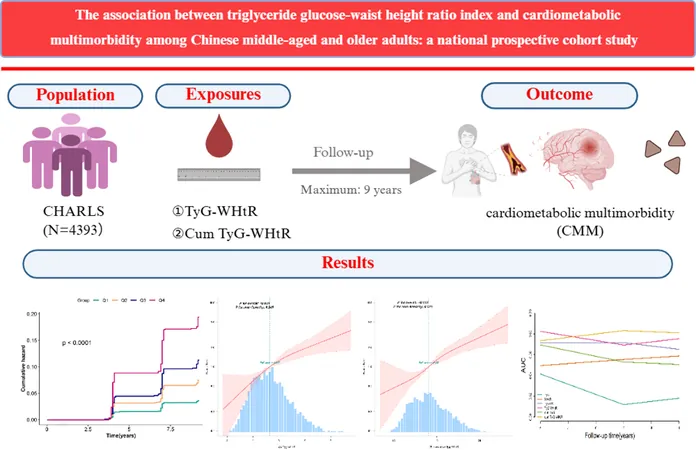
New research has introduced the Triglyceride-Glucose (TyG) index combined with the Waist-to-Height Ratio (WHtR) as a groundbreaking tool for assessing CMM risk. This study, utilizing data from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS), reveals a strong correlation between the TyG-WHtR index and CMM, highlighting a crucial gap in previous research.
Comprehensive Study Design and Findings
Analyzing data from over 4,000 adults aged 45 and older, this innovative study tracked participants across nearly a decade. Researchers discovered that those with higher TyG-WHtR indices faced significantly increased risks of developing CMM—a staggering rise in risk correlating with different tertiles of the index. The findings demonstrate that as the TyG-WHtR increases, so does the likelihood of CMM risk, with figures showing hazard ratios soaring as high as 3.13.
Methodology: A Deep Dive into Data Analysis
Employing advanced statistical techniques like Kaplan-Meier curves and multivariable Cox regression analysis, the study provided robust results confirming that elevated TyG-WHtR independently predicts the presence of CMM. This research also utilized time-dependent receiver operating characteristic analyses to solidify the predictive performance of the index.
A Potential Game-Changer for Public Health Strategies
The implications of these findings are vast. The TyG-WHtR index not only showcases a straightforward method for CMM risk assessment but also offers potential for early interventions. This could lead to preventative strategies aimed at mitigating the health burdens associated with multimorbidity, particularly in aging populations.
Challenges and Future Directions
While this study paves the way for improved health monitoring, it’s important to acknowledge certain limitations. Observational bias and reliance on self-reported data could affect the interpretability of results. Future studies should explore causal relationships and expand research beyond China to cater to diverse populations.
Conclusion: A New Frontier in Health Monitoring
As global obesity rates climb and populations age, the TyG-WHtR index emerges as a vital tool in the health assessment arsenal. This study underscores the pressing need for innovative approaches to detect and prevent CMM early. The findings could revolutionize how healthcare systems approach chronic disease management, highlighting the essential balance between individual health metrics and multimorbidity risks.




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)