Unlocking a Health Breakthrough: The Enzyme That Could Transform Cholesterol Management and Combat Inflammation!
2025-06-26
Author: Yu
Revolutionary Discovery in Cholesterol Management
In an exciting breakthrough, scientists at The University of Texas at Arlington have pinpointed a game-changing enzyme that can be "turned off" to regulate cholesterol levels effectively. This discovery holds immense promise for developing new therapies for various inflammatory diseases affecting millions of Americans.
Meet IDO1: The Enzyme Behind Inflammation and Cholesterol Issues
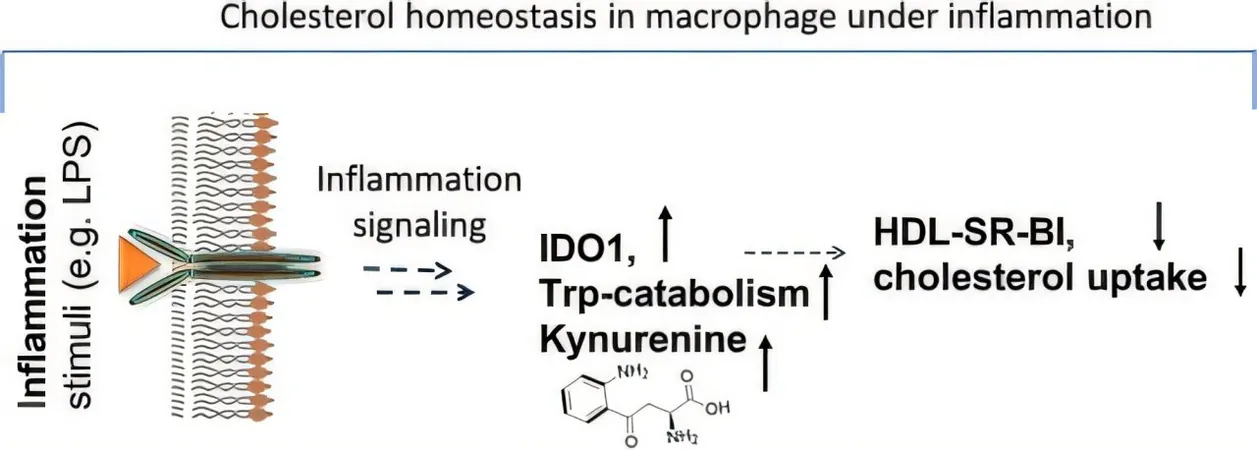
Lead researcher Subhrangsu S. Mandal is leading the charge in understanding the role of the enzyme IDO1. "By inhibiting this enzyme, we can manage inflammation in immune cells known as macrophages," says Mandal. This is crucial because inflammation is a silent killer, linked to a range of serious conditions such as heart disease, cancer, diabetes, and even dementia.
Inflammation: A Double-Edged Sword
While inflammation is the body’s natural defense mechanism, helping to fight infections and heal wounds, it can spiral out of control due to stress, injury, or infection. This abnormal inflammation can prevent macrophages from properly absorbing cholesterol, leading to chronic health issues.
The Kynurenine Connection
The research team—comprising experts including postdoctoral researcher Avisankar Chini and several dedicated doctoral and undergraduate students—discovered that during inflammation, IDO1 activates and produces a byproduct called kynurenine. This compound disrupts cholesterol handling in macrophages, aggravating health risks.
A Ray of Hope: How Blocking IDO1 Can Help
The fantastic news? When IDO1 is blocked, macrophages reclaim their ability to absorb cholesterol effectively. This indicates that reducing IDO1 activity could be pivotal in preventing heart disease and maintaining optimal cholesterol levels.
Exploring Additional Avenues for Treatment
Interestingly, the researchers also revealed that another enzyme, nitric oxide synthase (NOS), exacerbates the negative effects of IDO1. The inhibition of NOS presents a tantalizing possibility for further therapeutic approaches to manage cholesterol levels impacted by inflammation.
Implications for the Future: A New Frontier in Medicine
Mandal emphasizes the significance of these findings: "Too much cholesterol buildup in macrophages can lead to clogged arteries and a myriad of health issues. By comprehending how to thwart inflammation's effects on cholesterol regulation, we may unlock new treatment pathways for heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and beyond."
As this research unfolds, it could pave the way for innovative therapies that could not only change the lives of millions but also revolutionize the way we approach cholesterol management and inflammatory diseases!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)