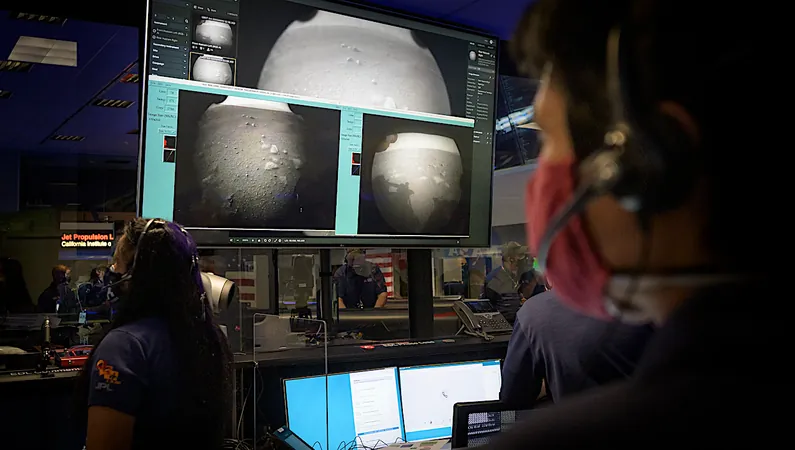

Unleashing the Power of Machine Learning in the Quest for Extraterrestrial Life
2025-05-22
Author: Arjun
Revolutionizing Astrobiology Through Data
In the thrilling search for extraterrestrial life, machine learning is emerging as a game-changer. Experts like Caleb Scharf from NASA’s Ames Research Center firmly believe that the marriage of advanced algorithms and astrobiological research could unlock unprecedented insights into the mysteries of alien life.
Transforming Data into Discoveries
At its essence, the hunt for life beyond Earth is about identifying the telltale signs—imprints that reveal whether life ever existed elsewhere. These signs come in the form of measurable data attributes that hold the key to understanding life’s potential fingerprints in the cosmos. With machine learning's analytical firepower, we can sift through vast quantities of this data, identifying patterns and correlations that might go unnoticed by traditional methods.
Two Extremes of Evidence Collection
Imagine two scenarios: on one end, we could stumble upon a thriving alien ecosystem, allowing us to confirm life’s existence directly. On the other end, we might gather a multitude of indirect clues that, while inconclusive alone, converge to suggest life is likely out there. This intricate dance of evidence requires not just a microscope, but a powerful telescope and complex modeling to map entire planetary systems over time.
Understanding the Bigger Picture
However, a mere collection of data points won’t suffice. For any claim of discovering life to hold weight, we need to weave together a coherent narrative that explains how such life thrives. For instance, if we discover an abundance of complex organic molecules under surprising conditions, it sparks curiosity, but without a clear origin story, we merely have a puzzle missing vital pieces.
A Future of Promising Possibilities
As we stand on the brink of new discoveries, the integration of machine learning into astrobiology isn’t just a possibility—it’s a necessity. With its vast potential to analyze and interpret data, we could find ourselves closer than ever to answering one of humanity’s most profound questions: Are we alone in the universe?


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)