
Uncovering the Hidden Secrets of Antarctica's Ice: A Journey Like No Other!
2025-03-26
Author: Jia
Introduction
An international research team has embarked on a groundbreaking expedition, deploying an unmanned submarine named "Ran" beneath the formidable ice of Antarctica. The goal? To capture the first in-depth maps of the glacier’s underside, unlocking essential clues about the looming threat of sea level rise.
The Mission of 'Ran'
Equipped with advanced sonar technology, "Ran" was programmed to venture into the Dotson Ice Shelf cavity in West Antarctica and skilfully navigate through the ice. Over an intensive 27-day mission, it traversed more than 1,000 kilometers beneath the glacier, exploring 17 kilometers within the cavity itself. This novel approach marks a significant shift from traditional methods relying on satellite data and ice core analysis to monitor glacier changes over time.
Dr. Anna Wåhlin, a Professor of Oceanography at the University of Gothenburg and lead author of the study, expressed the sense of discovery, stating, "Navigating the submersible into the cavity allowed us to create high-resolution maps of the ice’s underside. It’s akin to witnessing the back of the moon for the first time."
Understanding the Dynamics of the Dotson Ice Shelf
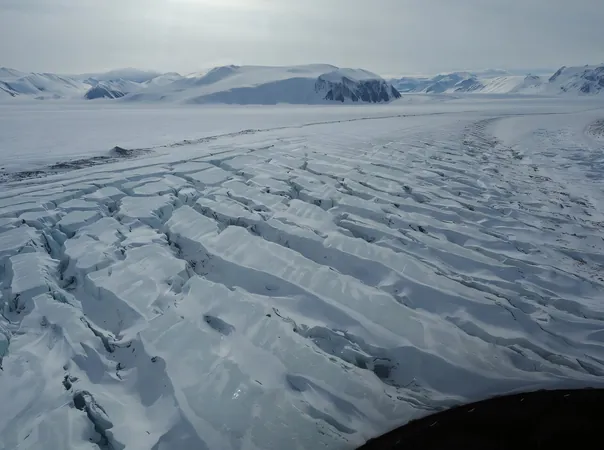
The Dotson Ice Shelf is crucial to discussions regarding future sea levels. Contrary to the perception of ice shelves as flat and inactive, they are dynamic entities that undergo continuous evolution. Floating above the ocean, these ice masses have cavities underneath, where significant processes occur.
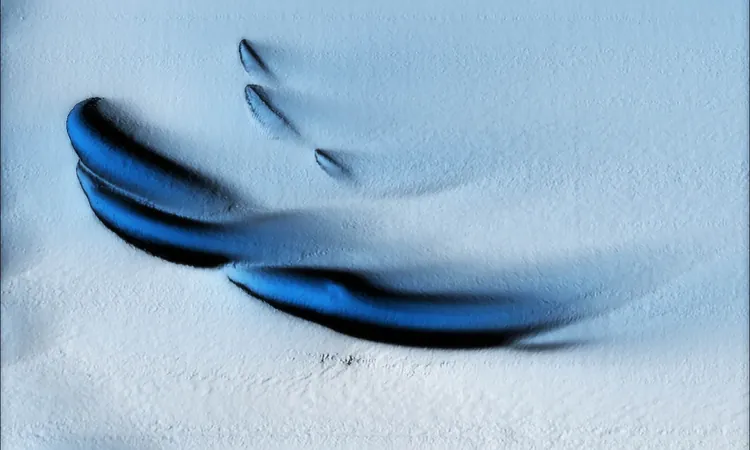
The Ran’s recent mission shed light on the complexities of these ice shelves, revealing insights that challenge previous scientific assumptions. The results showed that the base of the glacier was not purely smooth; instead, it exhibited an intricate landscape of peaks, valleys, and plateaus resembling sand dunes. Scientists theorize that these formations were sculpted by the movement of water influenced by the Earth's rotation, highlighting the urgent need for further exploration into the melting mechanisms at play.
Artistic Patterns Beneath the Ice
The expedition yielded astonishing visuals from beneath the ice shelf, leaving researchers adeptly intrigued yet puzzled by the textures and patterns encountered, which appeared more like artistic formations than natural ones. Prof. Wåhlin noted, "This exploration is not just about discovery; it serves as a wake-up call that many of our previous assumptions about how glacier undersides melt are misleading."
The images and findings prompt further investigations as scientists believe that understanding these unusual patterns will reshape predictions about ice melting and subsequent sea-level impacts. While melting ice shelves themselves do not contribute directly to sea-level rise, their degradation accelerates the flow of land-based glaciers, posing significant threats to coastal communities.
The Road Ahead: Future Research and Insights
Plans are underway for a follow-up survey in January 2024, with the team keen to capture any changes that may have occurred since their last expedition. However, the initial mission was not without setbacks; they managed just one successful dive before "Ran" vanished beneath the ice. Despite this, the valuable data acquired inspires hope for future research endeavors.
As humanity grapples with the ongoing climate crisis, every data point and insight derived from such explorations is critical. The University of East Anglia, in collaboration with the University of Gothenburg, continues to lead the charge in this vital field of study. As scientists peel back the layers of Antarctica’s icy enigma, they take another step toward understanding the impending shifts in our planet’s future.
The full study detailing these unprecedented explorations was recently published in the bulletin of the journal **Science Advances**, paving the way for further discussions and investigations into the intricate dance of ice and water hidden beneath the polar ice caps.
Stay tuned for more exhilarating updates as we continue to unravel the breathtaking mysteries of our planet’s climate!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)