Uncovering the Hidden Risks: Shocking Insights into Myocardial Infarction in Türkiye
2025-01-24
Author: Nur
Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) continue to devastate populations worldwide, accounting for about 17.9 million fatalities in 2019 alone, as reported by the World Health Organization. Among these deaths, myocardial infarction (MI) and strokes are the primary culprits, responsible for an alarming 85% of CVD fatalities. Specifically in Türkiye, circulatory system diseases top the charts, representing around 36% of total deaths. Notably, acute myocardial infarction (AMI) cases have soared, climbing to a rate of 39.38 per 100,000 individuals in 2021—a number that hints at a burgeoning health crisis.
Understanding Myocardial Infarction
Myocardial infarction stands out as one of the leading causes of death and disability, often serving as the first indication of coronary artery disease (CAD). AMI is the predominant form of coronary heart disease (CHD) and is influenced by an array of risk factors, including but not limited to age, gender, diabetes, obesity, blood pressure, smoking habits, and overall lifestyle choices.
Why Are Men More Affected?
Studies reveal that men exhibit a higher incidence of MI compared to women, coupled with greater fatality rates. Interestingly, diabetes also plays a detrimental role, as individuals with this condition are significantly more likely to die from AMI, especially in a setting like Türkiye, where diabetes prevalence is exceeding global averages.
Mental Health Matters
Lesser-known but equally important is the link between mental health and cardiovascular risks. Conditions like depression and anxiety have become recognized contributors to MI risk, while smoking exacerbates injury to the heart, fostering an environment ripe for adverse outcomes.
Obesity’s Role
With increased rates of obesity—particularly abdominal obesity—MI occurrences are becoming more prevalent among those afflicted. Obesity not only increases the likelihood of heart diseases but also complicates recovery from cardiovascular events. Comorbidities can further exacerbate the prognosis for MI patients; for instance, individuals with hypertension and asthma may experience worse outcomes than those with MI alone.
Focus on the Young
The study emphasizes that controlling risk factors in younger individuals is crucial due to their unfavorable long-term prognosis. Greater awareness and understanding of MI and its risk factors can significantly curtail mortality rates. Researchers aim to delve deeper into the mix of sociodemographic, biomedical, and lifestyle factors contributing to MI risks, utilizing advanced techniques like binary logistic regression and CHAID (Chi-Squared Automatic Interaction Detection).
A Deep Dive into Data
In this transformative study, researchers analyzed microdata obtained from the 2019 Türkiye Health Survey, which included more than 17,000 respondents. Notably, they concentrated on individuals aged 45 and above, considering the high risk associated with aging. The findings underscored that factors such as gender, marital status, education, health problems, and lifestyle behaviors were determinant indicators of MI likelihood.
The Alarming Findings
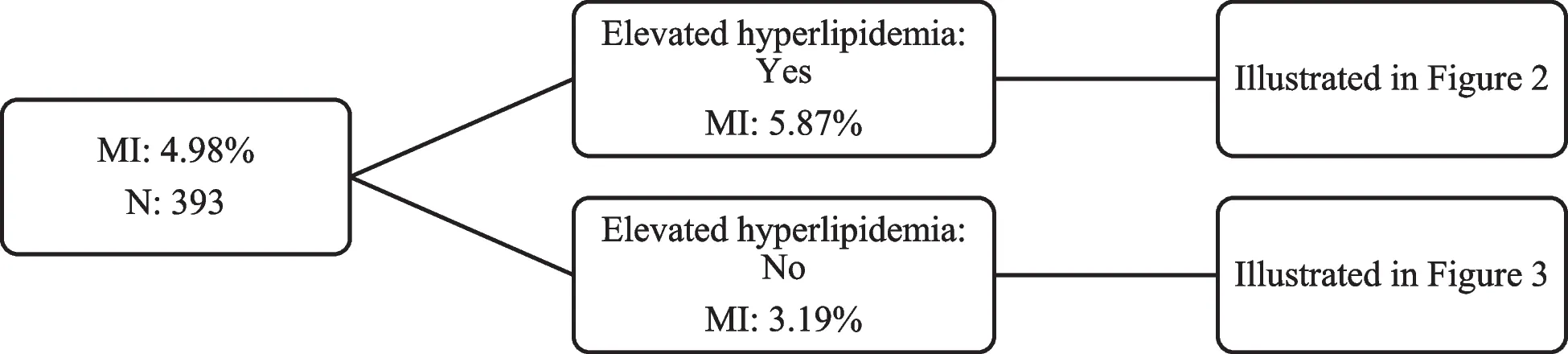
The analysis revealed the startling impact various factors have on MI risk. For instance, females had a 5% lower probability of experiencing MI than their male counterparts. Age-wise, those between 55 and 64 had a 1.8% greater risk than those aged 45-54. Additionally, individuals suffering from any health problem saw an alarming 4.8% increase in MI probability.
The Hypertension Link
The study identified hypertension as a common and critical risk factor. Globally, over half of MI cases are attributed to this condition, which underlines the pressing need for hypertension management and education, especially among younger populations.
Lifestyle Choices Matter
Key lifestyle factors such as physical activity levels, tobacco exposure, and alcohol consumption also displayed significant correlations with the incidence of MI. The apparent protective effect of regular physical activity and moderate alcohol consumption against MI requires broader public health strategies to promote healthier habits.
Addressing Limitations
However, researchers acknowledge certain limitations in their analysis, including the reliance on self-reported data and the exclusion of younger demographics. Future studies could benefit from a comprehensive approach that includes laboratory data and a variety of psychosocial factors.
Conclusion: Act Now!
To mitigate the rising tide of myocardial infarction in Türkiye, there is a clear and urgent necessity for targeted health interventions. By promoting education about cardiovascular risks and encouraging healthier lifestyles, especially among young adults, we can take proactive steps to tackle this growing crisis. Don’t become another statistic—prioritize your heart health today! Stay tuned for more insights as researchers continue to explore these critical connections between lifestyle, mental health, and cardiovascular disease. Your heart—your life—depends on it!





 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)