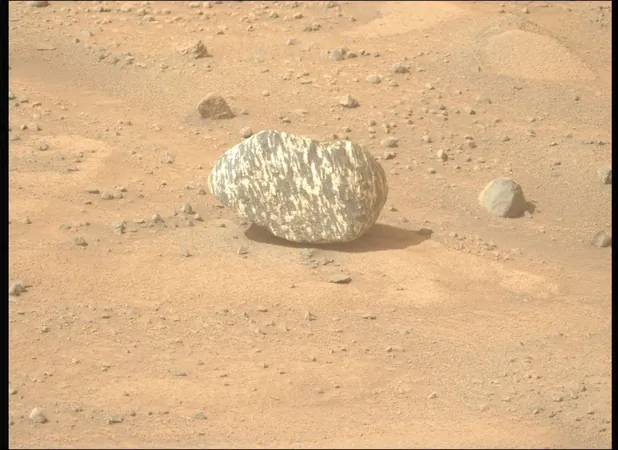

Uncovering Mars: The Mysterious Freya Castle Rock With Striking Black-and-White Stripes
2024-10-01
Author: Rajesh
Uncovering Mars: The Mysterious Freya Castle Rock With Striking Black-and-White Stripes
The excitement from the Mars Perseverance rover keeps intensifying as it traverses the Jezero Crater, a once watery haven on the Red Planet. Recently, Perseverance made an intriguing discovery—a rock featuring peculiar black-and-white stripes, aptly named "Freya Castle" by its mission team.
This striking geological specimen bears a remarkable resemblance to metamorphic rocks found on Earth, such as gneiss, marble, and schist. Experts like Jeffrey Kargel from the Planetary Science Institute suggest that Freya Castle could represent a high-grade metamorphic rock, possibly formed from minerals like feldspar. According to Kargel, the rock exhibits a structure known as "boudinage," a French term describing a sausage-shaped formation that occurs under immense pressure and heat as layered rocks like sedimentary types are compressed from above.
The Geological Puzzle of Jezero Crater
Freya Castle's uncharacteristic appearance amidst the prevalent dusty and sedimentary Martian landscape raises intriguing questions regarding its origins. Jezero Crater, which was formed by an enormous impact around 3.8 billion years ago, has shown evidence that water once flowed within its walls, creating a rich environment for sedimentation. Scientists have identified clay-rich deposits and other materials that confirm the past presence of liquid water—a significant clue in the search for microbial life.
But what can the discovery of Freya Castle tell us about the ancient Martian landscape? If confirmed as metamorphic rock, it could offer profound insights into Mars's geological history and conditions. Such rocks form under extreme conditions of heat and pressure, processes that have also shaped our own planet's crust. The formation of Freya Castle may be linked both to the ancient conditions on Mars and to impact events that shoved material to the surface.
Scrutinizing the Specimen: What Lies Beneath?
To understand Freya Castle's makeup more thoroughly, scientists are eager to conduct mineralogical and chemical analyses using the rover's onboard spectrometer. These examinations could answer vital questions about its formation and the geological processes at play on Mars. Kargel noted the potential of this discovery: if it indeed originated from Mars's lower crust, it could be one of the oldest records of Mars's history, possibly pointing toward the earliest signs of a hydrosphere that once flourished on the planet.
Yet, how did this intriguing rock come to rest in Jezero Crater? It's hypothesized that Freya Castle formed in a different location and was then propelled to the surface following an impact. Evidence of slight rounding on the edges could suggest that it was transported by water—a theory supported by the presence of river deltas and flow channels around the crater.
Could Freya Castle Be From Earth?
Interestingly, some daring hypotheses even entertain the possibility of an extraterrestrial origin. Could Freya Castle be a stray rock from Earth, flung into space during a cataclysmic impact? While fascinating, this theory seems unlikely given the complex dynamics required to launch a rock from our planet to Mars.
The emergence of Freya Castle at Jezero Crater is more than just another discovery; it’s a window into the ancient geological processes that have shaped Mars. As the Perseverance team continues its mission, every investigation of rocks like Freya Castle not only holds clues to the planet's past but also drives the quest to understand whether life ever existed on Mars or if it could exist in the future.
Stay tuned—if Freya Castle indeed holds the key to some of Mars's most profound secrets, we are on the brink of monumental revelations about our neighboring planet!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)