Uncovering Mars: Mysterious 'Martian Dog' and Other Hidden Secrets Beneath the North Pole!
2024-09-23
Author: Siti
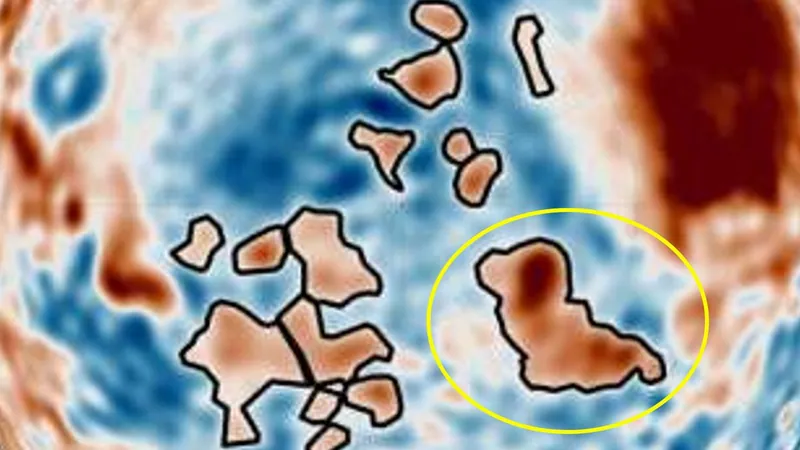
A stunning revelation has emerged from Mars, where a recent gravity map has uncovered dozens of enigmatic blobs hiding beneath the planet's north pole. Among these intriguing shapes is one that bears an uncanny resemblance to a dog, leading to a wave of speculation and excitement in the scientific community.
Researchers have taken a significant leap in our understanding of Mars by crafting the first true global density map of the planet. This unprecedented atlas is the result of a collaboration between data gathered from NASA's InSight lander and precise measurements from satellites like the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and the European Space Agency's Mars Express. These satellites measured gravitational anomalies that indicate hidden structures beneath the surface.
The most eye-catching features of the new map include 20 dense blobs located in the Borealis Basin, an area that was once an ancient seabed over 3 billion years ago. These blobs vary in shape and size, with densities ranging from 300 to 400 kilograms per cubic meter higher than the surrounding terrain, igniting curiosity about their composition and origin.
Bart Root, the lead author of the study from Delft University of Technology, posits that these structures could be volcanic formations or remnants of compacted materials from ancient meteor impacts. Intriguingly, there are no observable traces of these blobs at the surface, suggesting they have been hidden for eons.
The research team presented their groundbreaking findings at the Europlanet Science Congress in Berlin, which ran from September 8 to 13. Among the revelations, the gravity map has also confirmed the existence of a colossal 1,100-mile-wide blob beneath Olympus Mons, the tallest volcano in our solar system. This massive formation is believed to be a plume of cooled lava, indicating that Mars may still experience volcanic activity, or at least that its volcanism ended not long ago in geological terms.
Additionally, this new data could provide insights into the Tharsis plateau, an expansive Martian region rich in some of the planet's tallest volcanoes. As researchers continue to map the red planet's surface and sub-surface, they are revealing fascinating geological structures, including the recently uncovered "Labyrinth of Night" canyon.
Moreover, 2023 has already been a pivotal year for Martian discoveries. NASA satellites uncovered a significant layer of ice—over 2 miles thick—beneath Mars' equator in January, further highlighting the planet's complex geological history. In August, scientists made headlines with the announcement of a vast hidden ocean, capable of submerging the entire planet under a mile of water, trapped deep beneath the surface.
These recent findings are a tantalizing glimpse into the mysteries lurking under Mars’ surface, enhancing our understanding of the Red Planet and stirring imaginations about its potential to host life. As we continue our exploration, who knows what other secrets Mars holds? Stay tuned for more updates from the Martian frontier!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)