Transforming Avocado Waste into a Game-Changer for Food Emulsions
2025-06-26
Author: Mei
Revolutionizing Emulsification with Avocado Waste
When you think of emulsions, you might picture mayonnaise, creamy butter, or silky sauces. However, the art of emulsification extends far beyond just the culinary world, playing a crucial role in industries like cosmetics, paint, and pharmaceuticals. This intricate process involves blending two typically immiscible liquids, such as oil and water, into a stable mixture.
A Breakthrough at the University of Córdoba
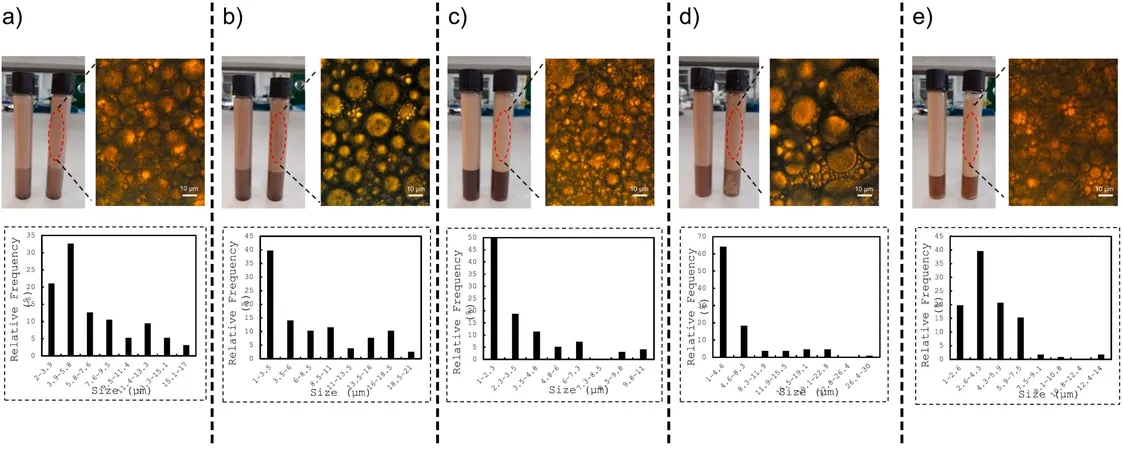
Researchers from the Biopren team at the University of Córdoba have made a pioneering discovery: they’ve transformed avocado pruning residues into a potent resource for creating emulsions. By extracting lignin—a key component of plant cell walls known for its adhesive properties—they've crafted a natural emulsifying agent.
Nanotechnology Meets Nature
This innovative team, associated with the Chemical Institute for Energy and the Environment (IQUEMA), has processed lignin into a fine powder on a nanometer scale. This newly developed emulsifier is remarkably efficient when mixed with water and soybean oil, a common base for various products.
Ramon Morcillo, the leading author of the study, highlights that traditional emulsifiers often rely on petrochemical sources. "Our biologically based emulsifier matches the performance of existing bioemulsifiers on the market," he insists.
Impressive Stability and Added Benefits
The results are astounding: this avocado-based emulsifier maintains the stability of mixtures for a whopping 27 days, preventing them from reverting to their separate liquid forms. But there's more—lignin is not just a stabilizer; it boasts natural antioxidant and antimicrobial properties, which could significantly enhance the shelf life of food products.
Unlocking the Power of Quercetin
Interestingly, the study published in the *International Journal of Biological Macromolecules* suggests boosting the emulsifier's benefits by incorporating quercetin, a beneficial compound found in many fruits and vegetables. However, its low solubility in water—which is critical for absorption in the body—poses a challenge.
To address this, the researchers encapsulated the emulsion, safeguarding its properties to improve bioavailability. Morcillo acknowledges, "While our study didn’t measure the bioaccessibility of quercetin, it’s a crucial area for future exploration." He emphasizes the importance of grounding the field of functional foods in scientific evidence.
A Sustainable Future?
This groundbreaking work not only presents a sustainable way to utilize avocado waste but also opens doors for healthier, longer-lasting food products. The implications are vast and could awaken a revolution in the food industry, making our everyday items better for both consumers and the planet.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)