The Transformative Era of 3D Cell Cultures in Biomedical Research: A Revolution Awaits!
2024-12-30
Author: Daniel
Introduction
For over a century, scientists have been delving into the enigma of cell growth and development, striving to propel medical research and drug development into new dimensions. Traditionally, research has relied on growing plant and animal cells in laboratory dishes, generating what is known as cell cultures. These cultures require meticulous care, with scientists ensuring that the cells receive adequate nutrients and optimal living conditions for their growth and replication. Such efforts have significantly broadened our understanding of cellular life and contributed to the development of groundbreaking drugs and vaccines for diseases, including cancer.
Limitations of 2D Cell Cultures
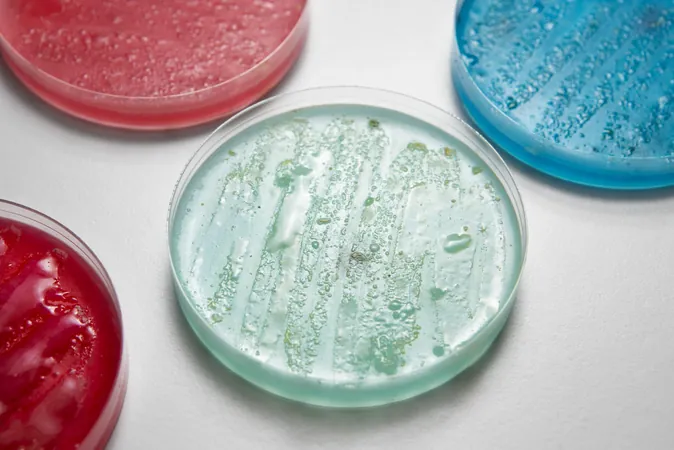
However, the conventional method predominantly involves two-dimensional (2D) cell cultures— a setup that confines cells to a flat surface. This limitation hampers the cells’ natural growth and behavior, leading to inaccuracies in experimental results. To overcome these constraints, researchers have innovated a revolutionary 3-dimensional (3D) cell culture system that allows cells to thrive in a more natural habitat. These advanced systems utilize spherical plates, gel-like hydrogels, and sophisticated bioreactors that regulate nutrient delivery and environmental conditions.
The Emergence of 3D Cell Cultures
The emergence of 3D cell cultures heralds a new era of biological research. This technology allows cells to grow in multiple directions, emulating their habitat in the human body and fostering interactions akin to what occurs in actual tissues. This method has inspired scientific exploration into how cell structures form, including complex formations that might mimic organ tissues.
Recent Findings in 3D Cell Culture
In a recent comprehensive evaluation of this technology, a team of scientists explored the integration of 3D cell culture in microbiology. Their findings are nothing short of astounding! They discovered that 3D cultures are proving pivotal in the development of vaccines, tumor modeling, and the creation of patient-specific cancer treatments. The study emphasizes that unlike their 2D counterparts, 3D systems offer a realistic setting that enhances the accuracy of drug efficacy evaluations, ultimately leading to better treatment strategies.
Advantages of 3D Cell Cultures
Moreover, cells maintained in 3D cultures exhibit more nuanced behavior, forming intricate structures and patterns similar to those observed in human tissues. This enhanced realism significantly boosts the fidelity of drug, treatment, and vaccine testing by effectively portraying how therapies interact with human cells and tissues.
Challenges Facing 3D Cell Cultures
Despite the promising advancements 3D cell cultures represent, the journey is fraught with hurdles. The cost of establishing and maintaining these cultures can be two to ten times higher than traditional 2D cultures. The technical complexity of designing and operating the necessary equipment also contributes to the slow integration of 3D cultures in biomedical research. Consequently, this delay could impede scientific progress, with pioneering researchers struggling to find qualified reviewers for their work and collaborators to replicate their findings.
The Future of 3D Cell Cultures
However, hope is on the horizon! Researchers assert that as 3D cell cultures provide more accurate models for drug tests, cancer research, and tissue engineering, they could significantly diminish reliance on animal models, expedite drug development, and ultimately yield safer, more effective treatments.
Conquering the Challenges
To conquer the challenges of cost, technical complexity, and the need for standardization, experts propose making 3D machining more accessible and efficient. The future beckons for further innovations, suggesting that researchers could explore the vast potential of 3D cell cultures in regenerative medicine and personalized cancer therapies.
Conclusion
As we transition into this transformative era, the question remains: Are you ready to witness the future of medicine evolve before your eyes?


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)