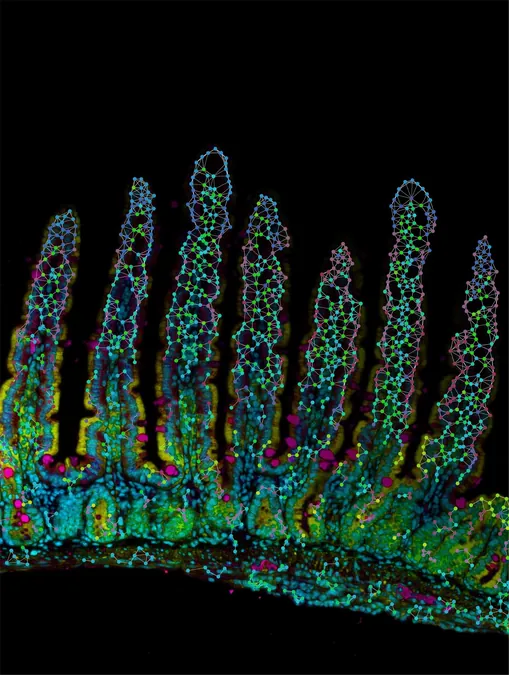
The Surprising Location-Based Roles of Immune Cells in the Gut Revealed by New Study
2025-01-22
Author: Yu
The human immune system operates like a carefully orchestrated military unit, with immune cells acting as specialized soldiers ready to combat diseases. A groundbreaking study published in Nature, spearheaded by researchers from the Allen Institute, La Jolla Institute for Immunology, and UC San Diego, has unveiled how the positioning of tissue-resident memory CD8 T cells in the small intestine determines their specific roles in immune defense.
These tissue-resident memory cells are critical components of our immune system, providing a local defense against re-infections and enlisting support from other immune cells as necessary. The research emphasizes that the location of these cells significantly influences their function, which could have far-reaching implications for developing more effective immunotherapies and vaccines.
Distinct Functions Based on Location
The study demonstrates that tissue-resident memory CD8 T cells exhibit diversity in functions correlated with their location within the gut's structure.
1. The Frontline Defenders: Positioned at the tips of the villi—finger-like projections in the intestine—certain CD8 T cells are like sentinels, equipped to immediately engage and eliminate invading pathogens. Their rapid response capability is crucial in preventing infections from taking a stronger hold.
2. The Reserves: In contrast, within the crypts—invagination areas of the gut—another subset of CD8 T cells remains on standby, ready to spring into action should the same pathogen invade again. These cells are essential for fostering long-lasting immunity.
"What truly amazed me was identifying how immune cells stationed in different gut areas serve specialized functions," remarked Dr. Maximilian Heeg, one of the study's lead authors. "Their strategic placement is the cornerstone of their operational capacity, a key takeaway from our findings."
This spatial specialization allows the immune system to react promptly to immediate threats while ensuring that a resilient backup defense is always ready for future challenges.
Dr. Ananda W. Goldrath, a leading figure in the research, added, "During an infection, immune cells infiltrate tissues not only to combat pathogens but also to aid in healing. Significantly, these cells interact with tissue cells to synchronize the immune response."
Exploring Microenvironments and Cellular Interactions
Through advanced transcriptional profiling, the researchers decoded the genetic directives that guide the behavior of tissue-resident memory CD8 T cells based on their unique locales.
Dr. Miguel Reina-Campos expressed his enthusiasm, stating, "Our innovative methods allow us to study immune cells in their natural settings with unprecedented detail. This opportunity could transform our understanding of immune responses."
These compelling insights pave the way for the design of enhanced immunotherapies and vaccines. By manipulating the pathways that govern the movement and functionality of these cells, scientists aim to boost the immune system's efficiency and improve overall health outcomes.
One of the highlights of this research was establishing causal links between well-known genes and the spatial roles of CD8 T cells. Alex Monell, a graduate student involved in the study, noted, "Expanding our CRISPR screening techniques will allow us to investigate multiple genetic influences on CD8 T cells simultaneously, ultimately aiming to optimize tissue-specific immunity."
Looking to the Future
This research underscores the significance of anatomical environments in driving immune responses and lays the groundwork for future studies aimed at exploring immune cell interactions within their niches. It holds promise for developing therapies targeting chronic diseases, infections, and inflammatory conditions by leveraging the intricate dynamics of tissue-resident memory immune cells throughout barrier tissues.
As we move forward, the focus will remain on harnessing this newfound knowledge to therapeutically fine-tune our immune responses, making it an exciting frontier in medical research. With these revelations, the potential for improving health outcomes and combatting disease through targeted immunologic strategies is greater than ever.




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)