
The Stunning Cosmic Event - A Pale Blue Supernova Dot in Distant Galaxy
2025-01-03
Author: Wei Ling
Introduction
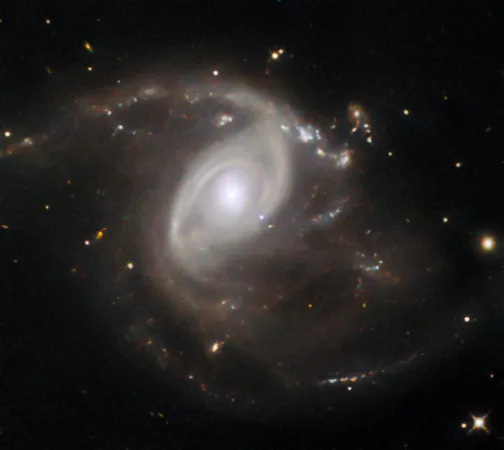
In an awe-inspiring display captured by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers have unveiled a spectacular image of the galaxy LEDA 22057, located approximately 650 million light-years away in the constellation Gemini. The striking feature of this image is a pale blue dot, the newly identified supernova SN 2024PI, a cosmic explosion that has intrigued astronomers and stargazers alike.
Discovery of SN 2024PI
Discovered by an innovative automated survey in January 2024, SN 2024PI represents the latest of over 10,000 supernovae cataloged by the survey, which meticulously monitors the northern half of the night sky every two days. Though this magnificent explosion has already faded in brightness since its initial discovery, its prominence in the spiral arms of the galaxy is a testament to the violent and beautiful processes that occur in the universe.
Understanding Type Ia Supernovae
Type Ia supernovae, like SN 2024PI, are particularly fascinating among the various types of supernovae observable in the cosmos. They arise from white dwarfs—remnants of stars that have exhausted their hydrogen fuel. After these stars evolve into cool, luminous red giants and expel their outer layers, the core remains as a white dwarf, which can reach astonishing surface temperatures exceeding 100,000 degrees Fahrenheit. Imagine a small sphere, the size of Earth, containing a mass equivalent to that of our Sun—that’s the density of a white dwarf!
The Mechanism Behind the Explosion
However, not every white dwarf will meet a spectacular end as a Type Ia supernova. For this explosive transformation to occur, the white dwarf must exist within a binary star system. By siphoning material from a neighboring star, the white dwarf can grow too massive to sustain itself, triggering a catastrophic reaction. The ensuing runaway nuclear fusion results in an explosive demise, creating a truly stunning astronomical event that can be observed across vast distances.
The Future of Our Sun
As we continue to study such celestial phenomena, it becomes evident that our own Sun will eventually follow a similar path approximately five billion years from now. It may someday evolve into a white dwarf, but whether it too will explode as a supernova remains uncertain. The universe, with all its mysteries, continues to captivate our imagination, reminding us of the vastness and dynamism of the cosmos.
Conclusion
So, if you're a fan of cosmic events and eager to learn more about the science behind these stellar phenomena, stay tuned for further celestial discoveries that are sure to keep sky enthusiasts on the edge of their seats!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)