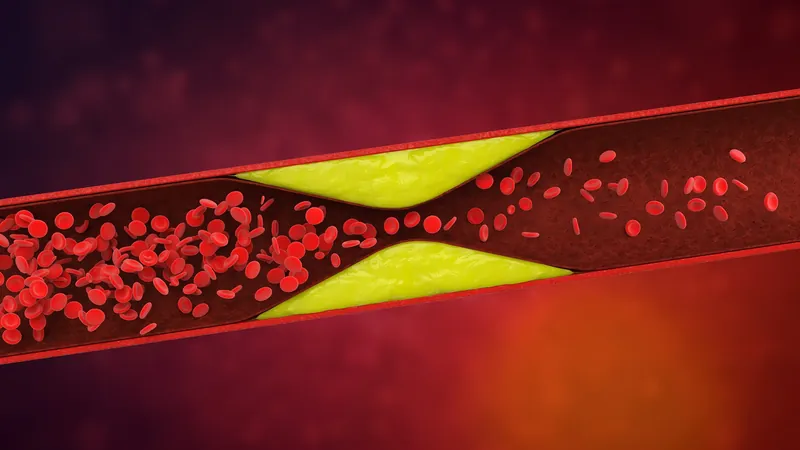
The Shocking Mutation Combo That Can Skyrocket Your Blood Clot Risk by 180%!
2025-06-08
Author: Jia
Understanding Blood Clots: Arterial vs. Venous
Ever wondered what's happening when blood clots form? Arterial clots form when plaque in blood vessels bursts, signaling injury to the body and activating platelets. This response can lead to catastrophic events like strokes or heart attacks. But have you ever heard of venous clots? These often form in the legs due to stagnant blood flow and can result in a dangerous condition known as pulmonary embolism if dislodged.
A Hidden Killer: The Silent Threat of Venous Thrombosis
"Venous thrombosis is surprisingly one of the leading causes of death globally," explains Bengt Zöller, a specialist at Skåne University Hospital. In Sweden alone, over 10,000 cases of venous thromboembolism occur annually, with numbers climbing. Factors like age, obesity, and lifestyle greatly contribute to this alarming trend.
Why Are Venous Clots on the Rise?
Age is a significant factor; approximately 10% of individuals over 80 experience a clot at some point. Additional conditions like being overweight or tall can increase risk due to reduced blood flow. Prolonged inactivity leads to slower circulation, making clots more likely. The physical structure of tall people’s veins also complicates things, as gravity plays a larger role in blood flow.
The Impact of Lifestyle on Clotting Risks
Interestingly, factors like high blood pressure and lipids don’t trigger venous clots as they do with arterial ones. Instead, obesity, particularly from a sedentary lifestyle, poses a greater risk. Studies also suggest that diets rich in ultra-processed foods can increase clotting risks, while consuming plant-based foods may lower them.
High-Risk Situations: When Blood Clots Strike
Certain situations can significantly heighten the risk of venous clots. Long flights, extended bed rest, surgeries, and certain infections can all cause blood flow reductions, resulting in increased clotting. The stakes are even higher during pregnancy due to changes in clotting factors.
Genetics Matter: The Discovery of a New Genetic Factor!
Zöller and his team have unveiled a groundbreaking genetic risk factor that could redefine our understanding of clot risks. By examining data from 30,000 individuals in Malmö, they identified three genetic variants—ABO, F8, and VWF—that, when combined, significantly elevate the risk of venous clots, matching the known risks of Factor V Leiden.
People with multiple genetic variants could find their risk skyrocketing, particularly those carrying five mutations, who face an astonishing 180% increased risk of venous thrombosis!
Your Next Steps: Preventing Blood Clots
So, what can you do to mitigate your risk? Here are some practical tips:
1. **Stay Active**: Avoid prolonged periods of sitting. Move around during long flights.
2. **Wear Support Stockings**: Especially useful during long periods of sitting or standing.
3. **Consider Anticoagulants**: In high-risk scenarios, like surgery.
4. **Be Cautious with Hormonal Treatments**: Especially if there is a family history of blood clots.
5. **Embrace a Healthy Lifestyle**: Kick the smoking habit, maintain a balanced diet, and engage in regular exercise.
6. **Stay Vaccinated**: It can help manage infections that might activate blood clotting.
Blood clots are more than just a medical term—they're a serious threat that can impact anyone. Understanding the risks, whether genetic or lifestyle-related, is crucial in combating this dangerous condition.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)