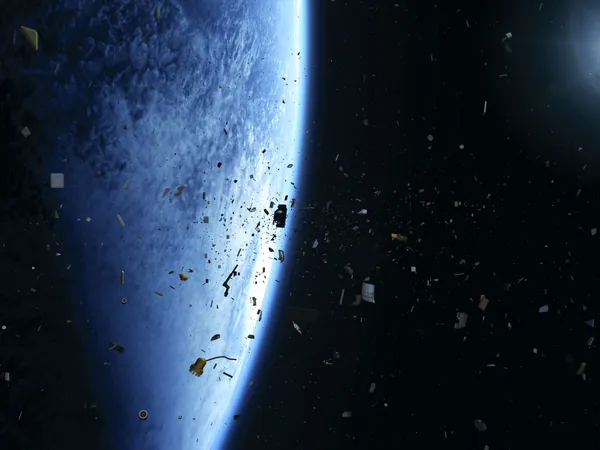

The Race to Eliminate Space Debris: A Comprehensive Roadmap Towards Zero Debris by 2030!
2025-01-15
Author: Siti
Why Space Debris is a Pressing Concern
Space debris, which can range from defunct satellites to tiny fragments of old spacecraft, jeopardizes both current and future missions. Collisions in orbit can cause catastrophic consequences, leading to more debris and economic losses. This persistent issue calls for immediate action and innovative solutions to ensure the safety of our space environment.
The Zero Debris Technical Booklet: A Game-Changer
The Zero Debris Technical Booklet serves as a collaborative guide that identifies crucial technologies necessary to reach the Zero Debris target. This document is significant, as it is the product of combined efforts from engineers, scientists, legal experts, and organizations committed to sustainable practices in space. Released within a year of the Zero Debris Charter's launch in November 2023, which has garnered support from 18 countries and over a hundred organizations, this Booklet stands as a testament to international cooperation in the fight against space debris.
The Six Pillars of the Zero Debris Initiative
The Booklet outlines six key technological goals essential for achieving the Zero Debris vision:
1. Prevent New Debris Generation
Establish robust protocols to ensure that no new debris is created, from small particulate matter to larger rocket bodies.
2. Minimize Collision Risks
Introduce measures to avoid collisions and break-ups that result in debris.
3. Enhance Space Traffic Management
Improve surveillance and coordination of space traffic to prevent accidents.
4. Promptly Clear End-of-Life Satellites
Develop methods to deorbit satellites efficiently after their missions are complete.
5. Ensure Ground Safety During Reentries
Mitigate risks associated with space objects re-entering the atmosphere to protect life and infrastructure.
6. Increase Awareness and Research
Advance our understanding of space debris and its environmental implications, particularly for our atmosphere and astronomical observations.
Strategies for Implementation: A Multi-Track Approach
Achieving the Zero Debris goal requires a robust, multifaceted technological strategy:
- Zero Debris Satellites
Development of more resilient, easily de-orbited satellites with improved materials and designs is critical.
- Launch Innovations
It is necessary to develop systems that limit or eliminate debris produced during the launch phase, including reducing propellant particle release and pyrotechnic hazards during satellite deployment.
- Operational Enhancements
Optimizing satellite operations and enhancing collision avoidance techniques through better tracking technologies will ensure ongoing safety during missions.
- Active Removal Strategies
As satellites near the end of their operational lives, active debris removal initiatives must be put into place to address the environmental impacts of reentry while ensuring no further debris is created.
ESA Leads the Charge Towards Sustainability
Under the banner of the European Space Agency (ESA), the Zero Debris initiative aims to redefine sustainable practices in space exploration. In the last decade, ESA has set bold new guidelines and established a dedicated policy to mitigate space debris risks across all its activities and collaborations.
A Vision Beyond Zero Debris
Achieving Zero Debris by 2030 is just the beginning. ESA envisions a future where space is not just clean but thrives on sustainability through in-orbit servicing, recycling, and a circular economy approach. This shift will enhance satellite longevity, reduce resource extraction demands, and pave the way for a sustainable future in both Earth and lunar orbits.
As stakeholders worldwide come together to tackle the daunting problem of space debris, the implications extend far beyond the immediate need for clean orbits; they reflect a commitment to responsible stewardship of our celestial environment for generations to come. Keep an eye on this crucial journey to a cleaner, safer space!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)