The Link Between Life's Essential 8 and Mortality in Alcohol-Related Liver Disease Patients: What You Need to Know!
2024-09-28
Introduction
Alcohol-related liver disease (ALD) is a critical health issue recognized as the most prevalent form of chronic liver disease globally. Alarmingly, cirrhosis due to alcohol misuse is responsible for 25% of all cirrhosis-related deaths, while ALD-related cancers account for 30% of liver cancer fatalities. Recent findings indicate that Life’s Essential 8 (LE8)—an emerging gauge of cardiovascular health—may be crucial in understanding outcomes for individuals grappling with ALD.
Understanding the Study
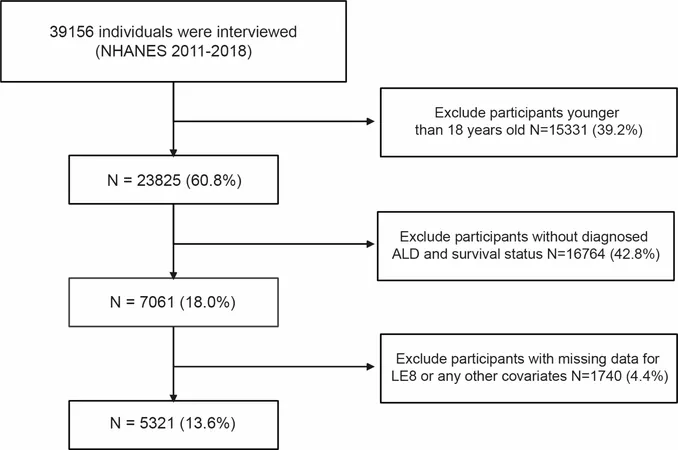
In an important study published in late 2023, researchers utilized data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) spanning from 2011 to 2018. They aimed to assess the relationship between LE8 — which encompasses dietary habits, physical activity, blood pressure, blood glucose, cholesterol levels, and more — and the mortality outcomes for patients suffering from ALD.
With a robust sample of 5,321 ALD patients, the results were striking. During an average follow-up of 63 months, the study documented 228 deaths from all causes. Intriguingly, those with high LE8 scores—indicative of better cardiovascular health—exhibited a staggering 53.7% decreased risk of all-cause mortality in comparison to their lower-scoring counterparts.
Why This Matters: The Human Cost of ALD
The significance of this research cannot be overstated. Presently, there are limited effective medical treatments for ALD, with abstaining from alcohol being the most common management strategy. The absence of early symptoms in many patients leads to late-stage diagnoses, which compromises treatment options and increases mortality risk. Therefore, understanding how lifestyle factors, tracked through LE8, correlate with longevity could pave the way for innovative management strategies benefiting a vast number of patients.
Key Findings
1. **LE8 Score and Mortality:** A higher LE8 score was inversely associated with all-cause mortality among ALD patients. For individuals scoring below a threshold of 71.12, each incremental improvement in LE8 scores corresponded to reduced cardiovascular mortality risk.
2. **Demographics Matter:** The most significant benefits from improved LE8 scores were observed among specific groups—particularly younger patients, women, and those with higher educational attainment.
3. **Lifestyle Factors Impacting Outcomes:** The study highlighted how lifestyle choices—encompassed in the LE8 scoring system—could influence ALD progression and mortality risk, stressing the need for broader public health initiatives promoting these healthy behaviors.
Future Directions and Implications
As the investigation establishes a compelling link between LE8 scores and mortality outcomes, it emphasizes the crucial interplay between cardiovascular health and liver disease management. It advocates the integration of health promotion strategies focusing on diet, exercise, and lifestyle modifications as a complementary approach to current ALD treatment protocols.
Conclusion
With a rising incidence of ALD globally, and its severe implications on health outcomes, understanding the role of cardiovascular health measures such as LE8 presents an opportunity for revolutionizing patient care. As research like this evolves, it propels forward a narrative that stresses the significance of comprehensive health strategies and prevention while providing hope for improved patient outcomes. The findings from this study illuminate a path forward in rethinking how we approach the treatment and management of alcohol-related liver disease—encouraging both healthcare providers and patients to prioritize cardiovascular well-being for enhanced longevity and quality of life.




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)