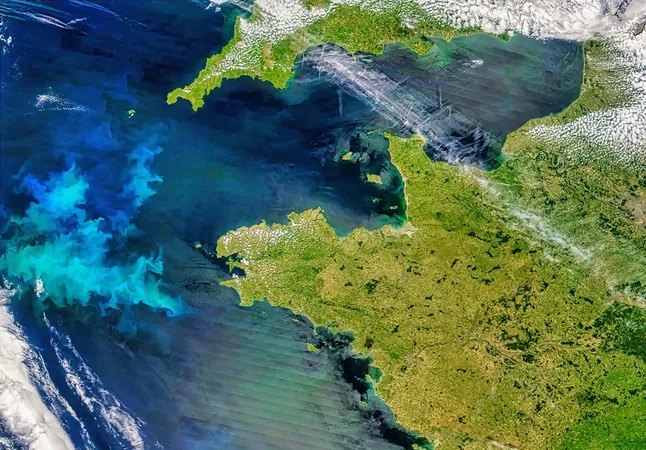

The Hidden World of Phytoplankton: An 'Invisible Forest' Thrives Amidst Climate Change
2024-09-26
Author: Rajesh
Phytoplankton: The Invisible Forest
Phytoplankton, the microscopic powerhouses underpinning nearly half of the Earth's primary production, are flourishing in what scientists refer to as an "invisible forest" deep within our warming oceans. These tiny yet vital organisms harness sunlight to produce energy through photosynthesis, playing a crucial role in addressing some of the most urgent environmental issues we face today, including ocean acidification, biodiversity loss, and disruptions to the global carbon cycle.
A Closer Look at Phytoplankton's Resilience
Recent research conducted by scientists at the University of Exeter has shed light on how phytoplankton populations are reacting to the various stresses imposed by climate variability. Their findings, published in the esteemed journal *Nature Climate Change*, highlight divergent responses among surface and subsurface phytoplankton communities regarding environmental changes driven by climate shifts.
Dr. Johannes Viljoen from Exeter’s Penryn Campus emphasized the significance of understanding these ecological dynamics, stating, “Phytoplankton form the foundational layer of the marine food web and are instrumental in removing carbon dioxide from our atmosphere.” He elaborated that deep-living phytoplankton, which thrive in low-light conditions, exhibit distinct responses to ocean warming compared to their surface-dwelling counterparts.
Increasing Subsurface Biomass Amid Warming Trends
Over the past decade, scientists have observed a remarkable increase in the biomass of subsurface phytoplankton, a change thought to be a direct reaction to rising ocean temperatures. In contrast, while the chlorophyll concentration of surface phytoplankton has decreased, their overall biomass has remained stable. Notably, an analysis spanning 33 years from the Bermuda Atlantic Time-series Study (BATS) in the Sargasso Sea revealed that the depth of the “surface mixed layer” is becoming shallower due to rapid oceanic warming.
Dr. Viljoen stressed the need for greater monitoring capabilities, remarking, “Our study underscores the limitations of satellite observations and points to an urgent demand for improved global tracking of phytoplankton beneath the surface.”
The Wider Impacts of Phytoplankton Changes
The study's co-author, Dr. Bob Brewin, discussed the broader implications of these shifts at the base of the marine food web. “Altering the dynamics of phytoplankton can reverberate throughout the ecosystem, affecting everything from microscopic zooplankton to larger fish and marine mammals,” he explained. Consequently, the future health of phytoplankton will profoundly influence biodiversity and the ongoing challenges posed by climate change.
With rising ocean temperatures, understanding the adaptability of different phytoplankton communities has become vital for predicting shifts within the marine food web. Scientists have underscored the importance of understanding how the vertical structure of phytoplankton may be impacted by warming and stratification of the upper ocean due to climate variability.
Recommendations for Enhanced Monitoring
As we navigate the challenges of climate change, the potential impacts on phytoplankton communities present significant consequences for climate change mitigation efforts. The ability of these organisms to sequester carbon dioxide is critical; if their populations decline due to warming seas, the ocean's efficacy as a carbon sink could be severely compromised, further exacerbating atmospheric carbon levels.
To combat these challenges, researchers are advocating for cutting-edge monitoring systems that transcend surface-level observations and utilize advanced technologies to delve deeper into subsurface phytoplankton populations. This enhanced monitoring will provide critical insights into how these key organisms are responding to rapid environmental changes, ultimately informing conservation strategies and climate initiatives.
Final Thoughts: A Call to Action
As scientists uncover more about this hidden “invisible forest,” it is clear that our understanding of phytoplankton is essential not only for marine conservation but also for combating climate change. The fate of these microscopic organisms carries profound implications; our oceans and, ultimately, our planet's future may very well rest on their delicate balance.
Join the conversation on environmental preservation by staying informed and advocating for the technologies and strategies that will protect our planet's vital ecosystems.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)