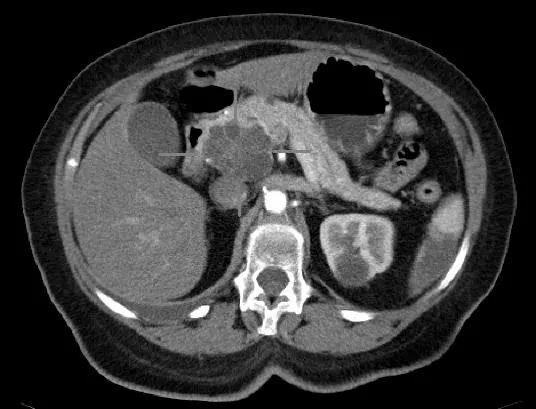
The Evolution of Pancreatic Cancer Screening: What You Must Know Now!
2024-12-29
Author: Daniel
Pancreatic cancer screening has undergone remarkable advancements in recent years, with research opening new doors to early detection. Recent studies underscore the importance of screening high-risk individuals, and exciting collaborations are underway to integrate genetic testing and artificial intelligence (AI) into screening protocols.
Dr. Michael Wallace, an interventional endoscopist at the Mayo Clinic Comprehensive Cancer Center, emphasizes the lifesaving potential of early detection. "We have high-quality studies from the U.S. and Europe that show screening can detect cancer at an earlier stage, leading to significantly improved survival rates," he states.
Who Needs Pancreatic Cancer Screening?
Current guidelines highlight that screening is crucial for individuals at heightened risk for pancreatic cancer. This includes those with a familial history of the disease or known genetic mutations. "The greater your family history, the greater your risk. We recommend screening if you have two first-degree relatives or three family members of any degree who have had pancreatic cancer," Dr. Wallace explains.
Unfortunately, many eligible individuals are not receiving the necessary genetic testing. "Only about one-third of people who qualify for genetic screening actually undergo it," Dr. Wallace points out. This is concerning given that recent Mayo Clinic studies suggest a connection between recent-onset diabetes, unexplained weight loss, and pancreatic cancer, particularly in individuals over 50. This form of diabetes is distinct from the more common type often associated with obesity. Anyone experiencing these symptoms should consult their doctor for a thorough evaluation.
How is Screening Conducted?
The primary methods for screening pancreatic cancer include MRI and endoscopic ultrasound, both of which should be performed at accredited medical centers. “Endoscopic ultrasound provides a detailed view of the pancreas, enabling biopsies if abnormalities are identified,” notes Dr. Wallace. Annual screenings are generally recommended, with MRI and endoscopic ultrasound alternating each year for optimal monitoring.
Breakthroughs in Pancreatic Cancer Screening
Innovative research is on the rise, particularly in the domains of genetic testing and AI technology. At present, genetically high-risk individuals only account for about 10% of all pancreatic cancer cases, while the remaining 90% are often diagnosed incidentally. Dr. Wallace elaborates on emerging research focusing on the analysis of pancreatic cysts—fluid-filled sacs that can harbor cancerous potential.
Additionally, AI plays a transformative role in this field. A groundbreaking study by Dr. Wallace and his team investigates AI's capability to swiftly assess MRI scans for signs of cancerous cysts—a task that typically requires significantly more time from radiologists. Preliminary findings indicate that the AI can perform this assessment in a fraction of the time, potentially revolutionizing the screening process.
Collaborative Research Efforts
Researchers are also exploring the relationship between common health indicators such as body weight, blood sugar levels, and cholesterol in predicting pancreatic cancer risk. Dr. Wallace suggests that routine checks for these indicators could serve as preliminary signals to recommend targeted screening for pancreatic cancer.
The amalgamation of genetic testing, AI advancements, and cutting-edge screening technologies is setting the stage for identifying pancreatic cancer at stages where treatment would be more effective.
In conclusion, progress in pancreatic cancer screening offers newfound hope for early detection and improved patient outcomes. Stay informed and consult with healthcare professionals if you or someone you know may be at risk—you could help save a life!
 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)