The Enigmatic Disappearance of Solar Wind on Mars: What Scientists Discovered!
2025-01-17
Author: Rajesh
Introduction
Mars, the intriguing planet known for its dusty landscapes and the possibility of ancient life, experiences dynamic atmospheric and climate interactions driven by solar wind—a continuous stream of charged particles that rushes from the sun's corona at speeds ranging from 400 to 1,000 kilometers per second. On Earth, these solar wind interactions create stunning auroras, but Mars lacks a global magnetic field, resulting in less dazzling, more diffuse auroral activity.
The December 2022 Event
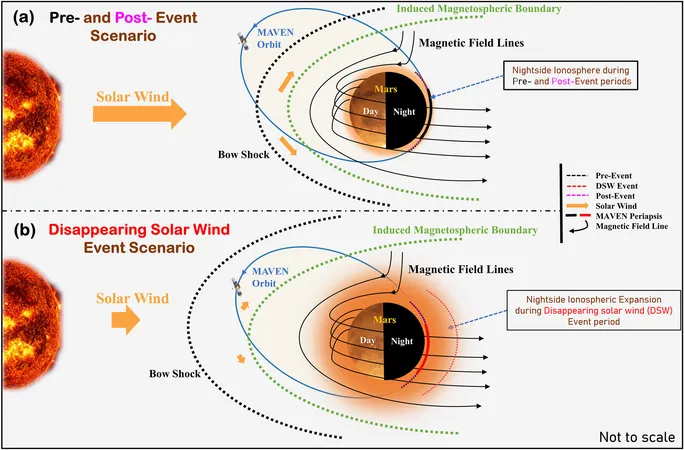
Recently, researchers observed a rare phenomenon where solar wind "disappeared" over a three-day span in December 2022, as detailed by NASA's MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN) mission. During this event, the solar wind experienced a significant gap caused by the overtaking of a slower wind by a faster one, creating a void that led to remarkable changes in the Martian atmosphere. The diminished solar wind pressure allowed Mars's atmosphere and magnetosphere to expand dramatically—tripling in size and producing a supersonic shockwave that encircled the planet.
Scientific Research and Findings
A team of scientists, including Professor Sumanta Sarkhel and Ph.D. researcher Lot Ram from the Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, examined the effects of this rare solar wind event in their research published in Geophysical Research Letters. They utilized data from several MAVEN instruments including the Solar Wind Ion Analyzer and Magnetometer to assess the ion densities, velocities, and overall conditions on Mars during the event.
Nighttime Plasma Density Increase
Their findings revealed substantial changes on the nightside of Mars, where plasma density soared in the ionosphere, reaching 2.5 times greater than normal. This increase is attributed to a notable pressure difference between the ionosphere (high pressure) and the solar wind (low pressure). This stark change resulted in an uptick in electrons and ions, with particular ions exhibiting dramatic density increases—10 times for nitrogen ions (N+) and a staggering 67 times for oxygen ions (O+).
Implications for Martian Exploration
Understanding these dynamics isn't just academic; it holds vital implications for future Martian exploration. The increased ionospheric drag during such solar wind events could necessitate adjustments to spacecraft orbits, ensuring safe navigation in the dense plasma environments.
The Importance of Understanding Solar Wind Events
Professor Sarkhel pointed out the significance of studying these solar wind disappearances, especially as they could illuminate Mars's history of atmospheric escape and climatic evolution. As Mars's magnetosphere-ionosphere system expands, the risk of atmospheric loss and interactions with radiation increases, further complicating our understanding of the planet's potential habitability.
Conclusion
Moreover, the study emphasizes the importance of comprehension of planetary space weather. Understanding these solar phenomena is crucial not only for safeguarding robotic missions but also for protecting astronauts who may one day venture to the Red Planet.
This rare solar wind event on Mars is not just a curiosity—it's a window into the complexities of space weather that could shape the future of planetary exploration and ignite enthusiasm for the mysteries that lie beyond our own world. Stay tuned as scientists continue to unravel the secrets of Mars, potentially paving the way for human presence on this captivating planet!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)