The Cosmic Show: How Black Hole Jets Ignite Stellar Explosions Across Galaxies
2024-09-29
Have you ever gazed at the night sky and pondered the mysteries of our universe?
Recent findings reveal that the death throes of stars are not as distant as one might think. Astronomers utilizing NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope have made a groundbreaking discovery: supermassive black holes are not just cosmic vacuum cleaners; they may also be the fireworks behind stellar eruptions!
What Triggers These Stellar Explosions?
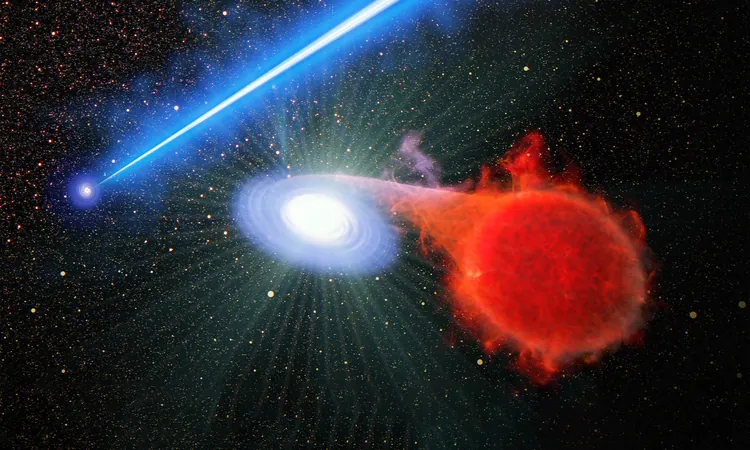
Imagine the heart of a sprawling galaxy, where a supermassive black hole sends out a jet of energy, akin to a blowtorch. This powerful jet can ignite stars in its vicinity, causing them to erupt in a dazzling display known as novae. But interestingly, these explosive events do not occur within the jet itself; they happen in the hazardous area surrounding it.
Alec Lessing, a leading researcher at Stanford University, expressed his excitement: “This discovery highlights gaps in our understanding of how black hole jets interact with their environments.”
Understanding the Nova Eruption Process
To grasp this phenomenon, consider a double-star system where an aging star transfers hydrogen to a white dwarf companion. As the white dwarf accumulates this material, it eventually leads to a violent nuclear explosion, known as a nova. Astonishingly, the white dwarf survives this cataclysm, resetting the cycle for more eruptions.
The M87 Galaxy: A Hotbed of Nova Activity
In their observations, Hubble identified that novae erupt twice as frequently near black hole jets than elsewhere in the galaxy. At the core of this research lies the M87 galaxy, home to a colossal black hole weighing 6.5 billion solar masses. This black hole creates a jet that extends 3,000 light-years, moving near light speed, and has been shown to increase nova activity in nearby stars.
This revelation raises questions: Are there simply more double-star systems in the vicinity of black holes, or are these stellar systems more prone to erupting? Lessing opined that the energy from the jets could be supplying additional hydrogen or altering the physics of mass transfer among the stars, leading to more frequent explosions.
Hubble's Mastery in Cosmic Observation
Hubble's recent observations involved revisiting the same region of the galaxy every five days, resulting in the most detailed imaging of M87 to date. The data revealed an astonishing 94 novae in just one-third of the galaxy's area captured, turning previous assumptions about their rarity on their head. In fact, one nova occurs in galaxy M87 every single day!
Considering there are around 100 billion galaxies in our observable universe, this translates to an incredible million nova eruptions happening every second.
The Role of Black Hole Jets as Catalysts
These findings suggest that black hole jets could be more than just destructive forces. They may act as cosmic catalysts, significantly shaping the stellar evolution of nearby systems. The jets' energetic outflow creates an environment conducive to high rates of mass transfer, leading to increased nova activity.
As researchers delve deeper into the intricate relationship between black holes and stars, the cosmos unveils more secrets, paving the way for a better grasp of universal dynamics. The bizarre interplay of gravity and energy might be just the beginning of a thrilling journey through our galaxy and beyond!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)