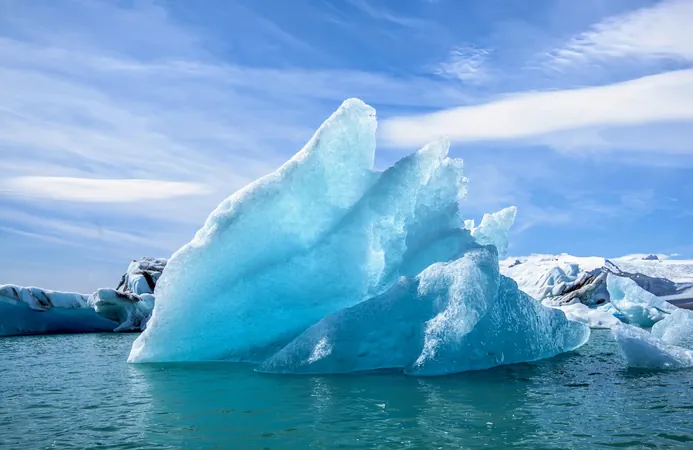

The Alarming Effects of Melting Arctic Sea Ice on Global Climate: What You Need to Know!
2024-10-28
Author: Rajesh
Arctic sea ice is disappearing faster than scientists ever anticipated, and a groundbreaking study has unveiled how this environmental crisis could severely disrupt climate systems worldwide. The melting ice not only impacts the Arctic itself but also triggers alterations in ocean circulation that can bring unexpected weather changes to regions far beyond.
Researchers are ringing alarm bells, warning that the consequences of diminishing sea ice may include increasingly severe weather events such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts. This urgent situation highlights the critical need to confront the human activities driving climate change.
A Journey Back in Time
In a fascinating twist, a team at the iC3 Polar Research Hub, led by climate scientist Mohamed Ezat, has delved into Earth's climate history by examining conditions during the Early Last Interglacial period over 100,000 years ago. This era was characterized by elevated global temperatures, reduced ice volumes, and sea levels significantly higher than today.
Their findings serve not only as a retrospective glance at climate dynamics but also provide vital clues about our current trajectory as Arctic sea ice continues to melt at an unprecedented pace.
The Fragile Balance of Earth's Climate
Ezat noted, 'Our discovery that increased melting of Arctic sea ice likely caused noteworthy cooling in Northern Europe in the past is alarming. It emphasizes how vulnerable Earth's climate is to even slight variations in temperature and ice cover.' The study connects historical warming and accelerated melting to shifts in sea-surface temperatures and ocean dynamics in the Nordic Sea, an area poised for significant impacts.
Are We Facing Ice-Free Summers?
Projections indicate that by 2050, the Arctic Ocean might experience ice-free summer conditions. Such drastic melting could lead to a domino effect of climatic changes that reverberate throughout the globe. The Nordic Sea, which lies between Greenland and Norway, stands out as a critical area expected to undergo dramatic alterations. This region is essential for moderating oceanic heat distribution and thus influences weather systems well beyond its geographical borders.
The Ripple Effects of Melting Ice
During the Last Interglacial, enhanced melting of Arctic ice profoundly affected sea-surface temperatures and ocean currents in the Nordic Sea. This melting altered the water's salinity and density, disrupting typical current patterns and causing significant shifts in how heat is distributed across oceans.
Learning from History to Navigate the Future
Utilizing advanced sediment core analyses from the Nordic Sea, researchers gathered invaluable insights into ancient ocean conditions. By studying biological and geochemical traces in these cores, they reconstructed historical data on sea-surface temperatures, salinity, and deepwater formations. These cores act as crucial time capsules, though many questions about past climate events remain unanswered.
Ezat remarked, 'Understanding the cooling events of the Last Interglacial and their processes is vital. We aim for our research to be a foundational reference for climate modelers seeking to understand current and future impacts of melting ice.'
Urgent Call to Action
In a recent open letter, dozens of climate scientists expressed grave concerns about the potential for significant changes in Atlantic ocean circulation that could lead to catastrophic, irreversible consequences. As Arctic ice continues to vanish, we must recognize the lasting effects of humanity’s choices.
The insights obtained from the iC3 Polar Research Hub's study not only illuminate our past but also aim to guide us toward a more sustainable future. The urgency of our climate crisis cannot be overstated, and it’s time for decisive action before it’s too late.
This pivotal research has been published in the esteemed journal Nature Communications and stresses the importance of learning from historical climate patterns to mitigate impending disasters. Don’t let ignorance doom our planet – stay informed and engaged!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)