Syphilis Resurgence in the U.S.: An Alarming Public Health Crisis
2025-09-12
Author: Arjun
A Shocking Upsurge in Syphilis Cases
Syphilis, a historically devastating sexually transmitted infection (STI), once peaked in the U.S. in 1947 before declining drastically with the arrival of penicillin. However, recent years have seen a distressing reversal, with syphilis cases skyrocketing by 80% since 2018. The exact causes of this alarming trend remain largely unexplored, raising concerns for public health.
The Dangerous Nature of Syphilis
Caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum, syphilis is primarily transmitted through sexual contact or from mother to child during pregnancy, resulting in life-threatening conditions like stillbirth. Often dubbed 'the great imitator,' it shares symptoms with a variety of illnesses, complicating its diagnosis. If left untreated, it can lead to severe complications affecting the heart, brain, and skin.
Understanding Epidemiological Trends (2018-2022)
Between 2018 and 2022, this study investigates syphilis trends across racial, ethnic, and geographical lines, aiming to uncover the behavioral factors contributing to rising rates. Insights gathered could inform effective public health interventions, especially for marginalized communities.
The Escalating STI Landscape
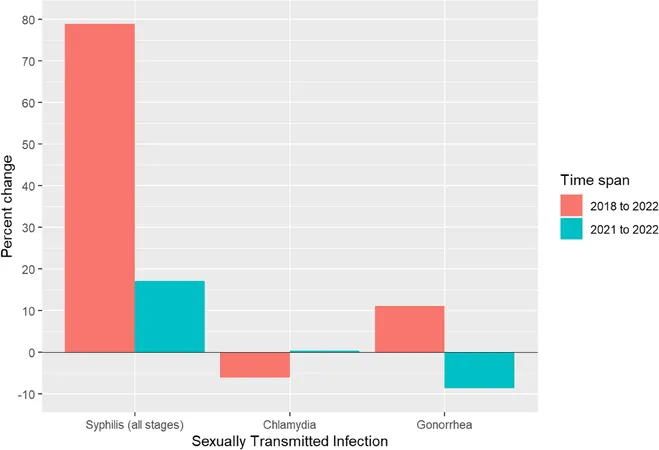
The latest data from the CDC reveals that while chlamydia cases showed a marginal decline, gonorrhea increased by 11%. Notably, syphilis reported a staggering rise of 78.90% over five years, underscoring its critical status as a public health concern.
Regional Disparities and Hotspots
Geographic analysis shows that the Midwest and Southern regions are suffering the highest rates of syphilis, particularly in states like South Dakota, calling for targeted interventions that consider local healthcare access and resource distribution.
Age and Gender Discrepancies
Data shows that syphilis disproportionately affects men, yet the number of cases among women has nearly doubled. The highest rates of infection were seen in individuals aged 25 to 29, indicating a worrying trend in younger demographics.
Racial and Ethnic Inequalities
All racial and ethnic groups are seeing increased cases, but specific populations, particularly American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN) individuals, have been hit the hardest, highlighting a dire need for stigma-free healthcare access.
Risky Behaviors Leading to Increased Infection
Individuals engaging in anonymous or intoxicated sexual activities have significantly higher odds of contracting syphilis, pointing to the need for education around safe practices.
Substance Use Correlating with STIs
Intriguingly, the misuse of substances shows a pattern within syphilis rates; those utilizing methamphetamines have the highest odds of infection, warranting attention in public health strategies.
Confronting Systemic Barriers
Current healthcare disparities are exacerbating high syphilis rates, revealing ongoing barriers faced by marginalized communities. Initiatives like enhancing mobile clinics and telemedicine services could bridge service gaps.
The COVID-19 Impact
The pandemic likely played a role in syphilis transmission through disrupted healthcare services, underscoring the need for immediate action to avoid a healthcare catastrophe.
Conclusion: A Call for Urgent Action
The resurgence of syphilis warns of an unfolding public health crisis that calls for increased surveillance, innovative outreach, and enhanced access to care. Addressing these disparities with culturally relevant solutions is crucial if we are to turn the tide on this alarming epidemic.




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)