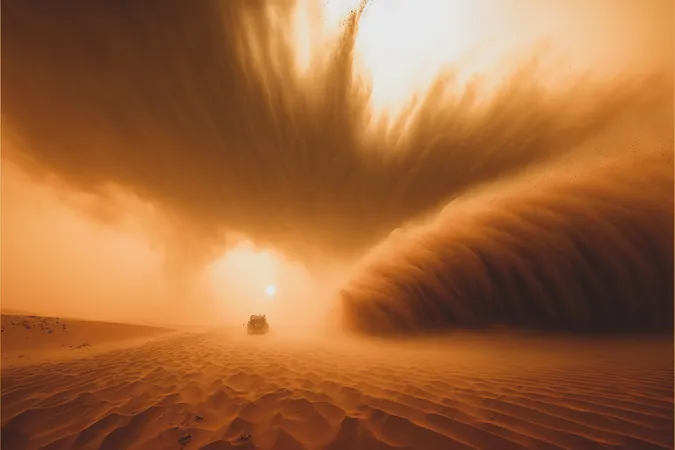

Surprising Connection: Saharan Dust Fuels Oceanic Life and Impacts Climate Change!
2024-09-20
Understanding the Relationship Between Sahara Dust and Marine Ecosystems
Recent research has unveiled a fascinating relationship between Saharan dust and the thriving ecosystems in our oceans. Iron, a critical micronutrient essential for various life-sustaining processes such as respiration, photosynthesis, and DNA synthesis, is often scarce in marine environments. As scientists dig deeper, they realize that enhancing the flow of iron into the oceans could significantly boost carbon fixation by phytoplankton, thereby influencing global climate patterns.
Sources of Iron in Oceans
The journey of iron into our oceans occurs through several processes: rivers transporting minerals, melting glaciers, hydrothermal activity, and prominently, the wind. However, not all iron reaches marine organisms effectively; only certain chemical forms are "bioreactive," making them accessible for uptake.
Insights from Dr. Jeremy Owens
Dr. Jeremy Owens, an associate professor at Florida State University and co-author of a novel study published in *Frontiers in Marine Science,* reveals a compelling discovery that iron bound to Saharan dust undergoes notable transformations as it traverses vast distances. "The farther it travels, the more bioreactive the iron becomes," states Owens, indicating that atmospheric chemical processes enrich this vital nutrient over time.
Research Methodology
In their research, Owens and his team analyzed drill cores from the Atlantic Ocean floor, sourced from the International Ocean Discovery Program (IODP). This initiative seeks to enhance our understanding of climatic changes, geological processes, and even the origins of life. Their focus centered on four specific drill cores, strategically selected based on proximity to the Sahara-Sahel Dust Corridor—a key dust source stretching from Mauritania to Chad.
Key Findings
The findings made waves in marine science: the cores revealed a higher concentration of bioreactive iron in regions farthest from the Sahara. This suggests that a significant portion of this vital nutrient is consumed by organisms in the water column before it can settle to the sediments below. “As the dust travels, it transforms, becoming more bioreactive," says Dr. Timothy Lyons of the University of California at Riverside and concluding author of the study. "This process highlights a crucial link between terrestrial and marine ecosystems.
Broader Impacts and Conclusion
Interestingly, this research illustrates that dust reaching far-off areas such as the Amazon basin and the Bahamas is likely enriched with particularly soluble iron. This enriched dust promotes marine life and could potentially have substantial implications for understanding climate dynamics. As global climate change intensifies, the interplay between atmospheric phenomena and marine health becomes critically relevant. The tale of Saharan dust, carried by winds across thousands of kilometers, showcases nature's intricate connections, reminding us of the delicate balance sustaining oceanic life and overall planetary health.
Exploring Earth's Natural Processes
Are you ready to explore how Earth's natural processes influence our climate? The findings are just the tip of the iceberg!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)