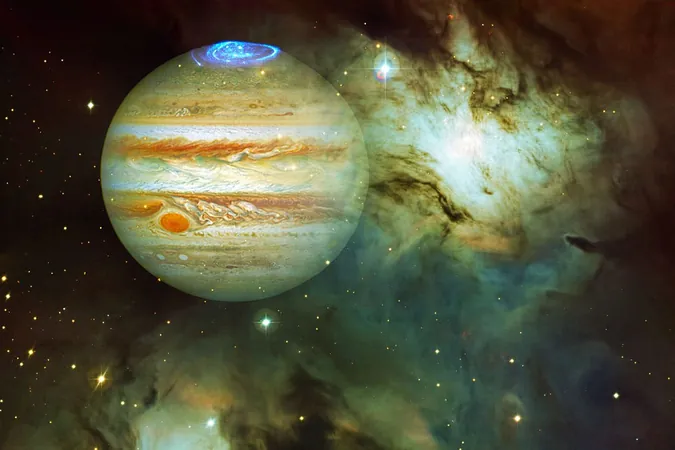

Supersonic Winds Whirl at 33,000 km/h Around the Exoplanet WASP-127b: A Must-Know for Space Enthusiasts!
2025-01-26
Author: Mei
In the endless expanse of the universe, exoplanets are revealing astonishing and extreme characteristics that keep scientists intrigued and eager for discovery. Among these celestial bodies is WASP-127b, a gas giant that captivates astronomers not just because of its sheer size but also due to its extraordinary atmospheric dynamics. Located approximately 520 light-years away, this fascinating world orbits a star similar to our own Sun, propelling scientists into a frenzy of excitement as they explore its unique traits.
What Makes WASP-127b So Remarkable?
WASP-127b stands out as one of the most fascinating gas giants we’ve encountered. With a diameter nearly 30% larger than Jupiter yet only possessing about 16% of Jupiter's mass, it is classified as one of the puffiest and least dense planets discovered to date. This remarkably low density suggests an atmosphere that is significantly expanded and less compact compared to other planetary formations, evoking curiosity about its composition and development.
As a member of the "hot Jupiter" club, WASP-127b basks in intense heat, with atmospheric temperatures soaring beyond 1,000 kelvins (730°C) and even reaching a blistering maximum of about 1,400 kelvins (1,127°C). This extreme thermal environment plays a critical role in dictating the planet's peculiar characteristics and behaviors, further enhancing its allure.
Unbelievable Wind Speeds: How Fast is Fast?
The most astonishing feature of WASP-127b is its staggering wind speeds. Researchers have measured jet streams at the planet's equator racing at an astounding 33,000 km/h. To put this in perspective, Earth’s jet streams can reach speeds of up to 442 km/h, making the winds of WASP-127b some of the fastest ever recorded on a planetary scale.
These ferocious winds are primarily fueled by the relentless radiation emitted from its host star, which continuously bombards the day side of the planet. This influx of energy triggers wild atmospheric currents, although scientists speculate that additional factors may contribute to these extreme wind patterns.
Groundbreaking Discoveries: What Researchers Found
A recent pivotal study published in the journal *Astronomy & Astrophysics*, led by astrophysicist Lisa Nortmann and her colleague David Cont, has stirred excitement within the astrophysics community. Utilizing CRIRES+, an advanced instrument integrated into the Very Large Telescope at the European Southern Observatory in Chile, they have compiled groundbreaking observations of WASP-127b.
Nortmann expressed amazement at the "astonishingly high" wind speeds, indicating that such findings are pivotal in challenging and refining existing models of exoplanet atmospheres. Co-author David Cont highlighted the complexities involved in understanding the drivers of these extreme winds, given that various elements play a role in shaping wind patterns across different planets.
What Lies Ahead for Exoplanet Research?
Determining the underlying mechanisms behind the supersonic winds on WASP-127b is a pressing focus for researchers. As they continue to investigate the forces affecting wind behaviors in alien atmospheres, they anticipate future discoveries that could illuminate weather patterns on other distant worlds. The intricate interactions occurring on WASP-127b might unlock vital insights into the atmospheric conditions that characterize planets across the universe.
Each new discovery about exoplanets expands our understanding of the cosmos, revealing how much remains unknown. The enigmatic nature of WASP-127b serves as a powerful reminder of the vast secrets our universe holds, and it encourages ongoing exploration into these captivating celestial phenomena. For those who are passionate about space exploration and cutting-edge scientific advancements, delving into these extraordinary phenomena leads us to ponder the mysteries waiting to be uncovered among the stars.





 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)