Stark Health Disparities Uncovered in the US During COVID-19: A Deep Dive
2025-08-15
Author: Jia
A Comprehensive Study Amidst a Crisis
This investigation delves into critical trends and disparities in health outcomes and access to care across the United States from 2019 to 2022, an era marked by the challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic. Leveraging data from the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS), researchers aimed to highlight how this unprecedented time affected various demographic groups.
Shifts in Survey Methodology Due to COVID-19
Initially conducted through in-person interviews, the NHIS adapted by moving largely to telephone surveys due to health concerns arising from the pandemic. This transition captured vital health information while navigating the challenges posed by social distancing.
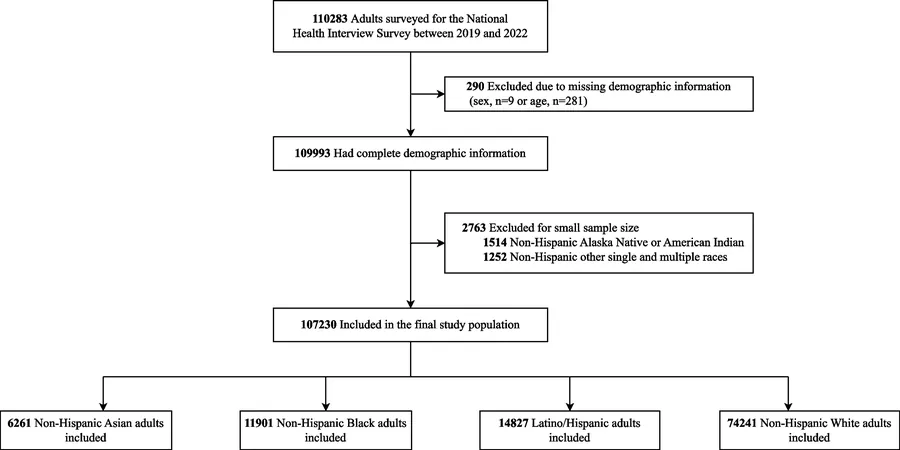
Diverse Population Profile and Key Findings
The study analyzed data from over 107,000 adults, showcasing notable racial and ethnic disparities. Black and Latino individuals displayed a higher prevalence of poor health outcomes and mental health disorders compared to their White and Asian counterparts.
Health Status: Who's at Risk?
In 2019, 21.6% of Black individuals reported poor or fair health, a stark comparison to just 9.6% of Asians. Alarmingly, these figures remained largely stagnant from 2019 to 2022, emphasizing the ongoing need for targeted health interventions.
The Mental Health Crisis Worsens
The pandemic exacerbated mental health struggles, particularly among White individuals, who saw a significant rise in diagnosed depression and anxiety. By 2022, 38.2% of low-income Whites reported mental health issues, compared to just 5.1% among high-income Asians.
Challenges in Accessing Care
Access to healthcare also featured alarming disparities. While the uninsured rate among Whites decreased, rates for Black and Latino groups remained alarmingly high. In 2022, nearly 28.3% of low-income Latino individuals were uninsured.
Cost Barriers Keeping Care Out of Reach
Over 16% of Latino respondents reported delaying necessary medical care due to costs, highlighting the financial barriers that persist across racial lines.
Persistent Racial Disparities Call for Action
Despite some improvements in access to insurance among certain groups, the disparities in health status and affordability persisted, uncovering the urgent need for systemic reforms.
Recommendations for a Healthier Future
To bridge these gaps, targeted health policies that focus on mental health resources, comprehensive healthcare access, and economic support are essential. The pandemic has underscored the vulnerability of many individuals, pointing to a path forward that emphasizes resilience and accessibility.
Conclusion: Lessons Learned from a Global Health Crisis
The evidence from this study reveals the profound impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on health and healthcare access across different racial and ethnic groups. As we move forward, it's crucial to recognize these disparities and implement strategies that prioritize equitable health outcomes for all.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)