Star-Shaped Brain Cells Unlock New Hope for Personalized Bipolar Disorder Treatments
2025-09-10
Author: Siti
A Deep Dive into Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder, often described as "manic-depressive illness," is a severe mental condition that has even touched the lives of iconic figures like artist Vincent van Gogh. This disorder is marked by alternating episodes of mania and depression, impacting about 1% to 2% of the global population. Alarmingly, individuals with bipolar disorder face a suicide risk that is 10 to 30 times higher than those without the illness.
The Urgent Need for Personalized Treatments
Despite lithium being the cornerstone treatment for bipolar disorder, individual responses vary dramatically, highlighting a pressing need for tailored therapeutic options. Recent groundbreaking research from a team at KAIST, led by Professor Jinju Han, aims to tackle this issue by exploring the metabolic roles of astrocytes—star-shaped brain cells integral to neuron support.
Astrocytes: The Unsung Heroes of the Brain
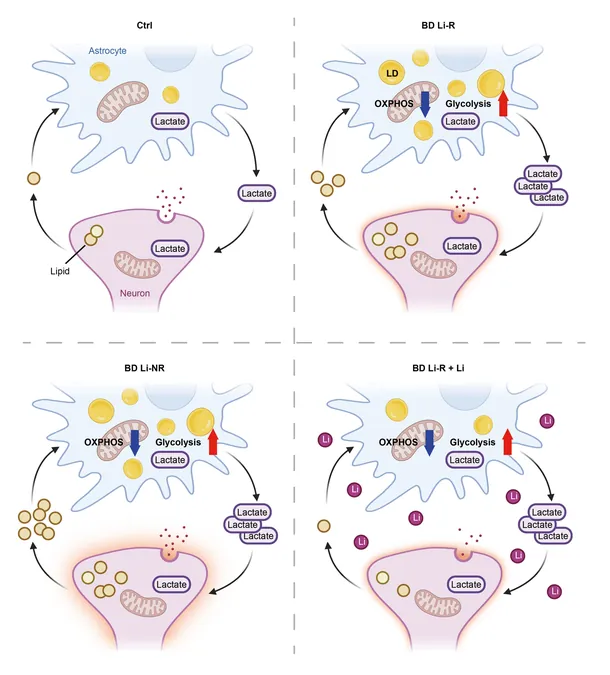
This innovative study steps away from traditional neuron-focused research, spotlighting astrocytes which constitute roughly half of the brain’s cellular architecture. Professor Han’s team has discovered that astrocytes are pivotal in regulating energy metabolism specific to bipolar disorder, particularly concerning how patients respond to lithium.
Transformative Discoveries Through Stem Cell Research
The researchers made significant strides by differentiating induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from patients into astrocytes. This meticulous process revealed that the astrocytes' energy metabolism dramatically shifts based on their responsiveness to lithium—offering a fresh perspective on treatment efficacy.
Metabolic Differences: A Game-Changer for Treatment
Notably, those patients who did not respond to lithium exhibited alarming metabolic abnormalities, including excessive lipid droplet accumulation, reduced mitochondrial function (which serves as the cell's powerhouse), and heightened glucose breakdown leading to surplus lactate production. Conversely, lithium-responsive astrocytes demonstrated a decrease in lipid droplets post-treatment, underscoring the metabolic divide between patient groups.
Paving the Way for New Treatments
These groundbreaking findings firmly establish astrocytes as crucial players in the metabolic landscape of bipolar disorder. They illuminate why some patients don’t respond to conventional lithium therapy and pave the way for innovative, personalized treatment strategies tailored to individual metabolic profiles.
A New Era of Hope for Patients
Professor Han expressed optimism about these findings, stating, "The development of new treatments targeting astrocytes is now possible, which could provide better treatment strategies for patients who do not respond to existing medications." This research not only opens new avenues for therapy but also offers hope for millions affected by bipolar disorder.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)