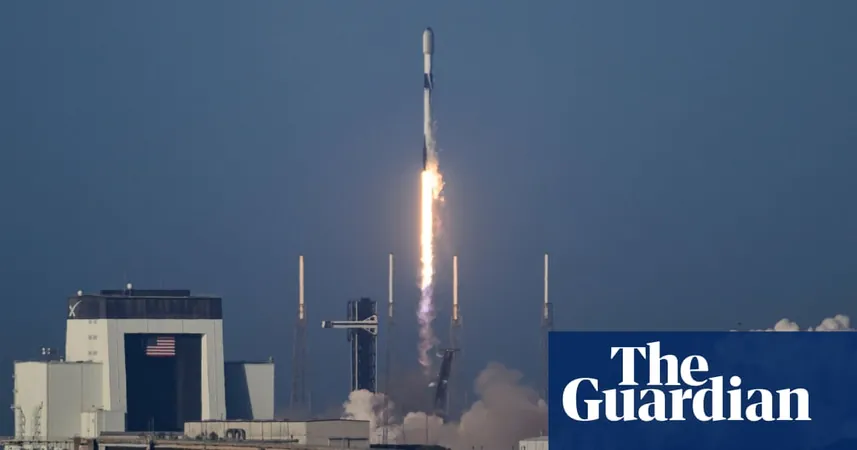

Shocking Truth Revealed: Space Launches and Re-Entries Are Polluting Our Air!
2024-11-01
Author: Jia
Introduction
It’s no surprise that rocket launches produce significant air pollution, but many are totally unaware of the hidden dangers posed by the re-entry of discarded spacecraft and rocket components. A recent groundbreaking global inventory has shed light on this pressing issue, revealing the alarming extent of air pollution linked to space activities from 2020 to 2022.
The Study's Findings
This comprehensive study meticulously documented the pollution generated from all phases of rocket activities, covering a staggering total of 446 launches. It also tracked the hazardous re-entries of 3,622 objects, including satellites and rocket debris, as these materials heated up and broke apart in the atmosphere. Between 2020 and 2023, these events accounted for nearly 12,000 tonnes of air pollution, adding to the already concerning levels attributed to the 63,000 tonnes of rocket propellants consumed in 2022 alone.
Insights from Lead Researcher
Lead researcher Dr. Connor Barker from University College London (UCL) revealed some surprising insights: “Many rocket manufacturers and space agencies guard this information jealously. We had to rely on a variety of creative sources, from YouTube launch live streams to databases curated by passionate space enthusiasts.”
Historical Context
Historically, between the late 1960s and 2016, between 100 to 200 space objects were launched annually. However, the rise of megaconstellations, such as Starlink and OneWeb, has sent those numbers skyrocketing. These communications systems require low Earth orbits to minimize signal delays and ensure global connectivity, leading to unprecedented levels of space launches.
Increasing Debris and Emissions
“What took us aback was how rapidly the amount of debris falling back to Earth is increasing — we're witnessing a dramatic uptick in discarded rocket parts and retired satellites,” Dr. Barker elaborated. “It’s astonishing to think that the first of these megaconstellations only began launching in 2019 and their emissions are climbing at an alarming rate.”
Composition of Pollutants
The pollutants released during rocket launches vary based on the types of propellant used but can include harmful substances like soot particles, aluminum oxides, nitrogen oxides, and even chlorine. Moreover, the extreme temperatures encountered during re-entry lead to a chemical reaction in the atmosphere that results in additional nitrogen oxides formation, along with tiny metal-oxide particles produced from the disintegration of objects.
Conclusion and Call to Action
As space activities surge with renewed vigor and ambition, the environmental implications cannot be overlooked. The call for stricter regulations and more sustainable practices in the space industry grows louder with each new launch. How will space agencies respond to the growing fear that our ventures into the cosmos might be raining pollutants back down on our planet? The time for accountability is now.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)