Shocking Surge: The Rising Toll of the 2024 Dengue Outbreak in Bangladesh
2025-04-02
Author: Jia
Dengue fever, a mosquito-borne viral infection, presents an escalating global health crisis, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions where approximately 3.9 billion individuals are at risk. The World Health Organization estimates that 400 million infections occur annually, culminating in around 21,000 fatalities each year. Notably, Bangladesh has emerged as a significant hotspot for dengue fever, with a complex history of outbreaks that date back to the 1960s.
The nation experienced its first notable outbreak in 2000, which resulted in 5,551 hospitalizations and 93 deaths. Since then, dengue has continued to ravage the country, with evolving strains leading to an alarming increase in cases every year. The history of serotypes contributing to these outbreaks has seen a shift, with DENV-1, DENV-2, DENV-3, and DENV-4 all playing respective roles over the decades. In 2023, the country witnessed the deadliest outbreak globally, with over 321,000 hospitalizations and 1,705 deaths recorded.
As we steer into 2024, Bangladesh is facing yet another severe dengue outbreak. Preliminary reports indicate that by October 2024, the nation had recorded 41,810 cases and 210 deaths, with actual numbers likely being higher due to reporting inconsistencies. The previous year’s outbreak marked a critical turning point in the clinical landscape of dengue fever in the region, necessitating detailed and continuous evaluation of ongoing cases to understand their severity fully.
Study Overview and Objectives
Amid rising concerns, a recent multicenter observational study aimed to document and analyze the clinical and epidemiological characteristics of the dengue outbreak during the rainy months of 2024. The study was conducted across four major hospitals: Dhaka Medical College, Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College, Mymensingh Medical College, and Chittagong Medical College, offering a comprehensive perspective on the national crisis.
The focus was to include patients aged 12 years and above, confirmed as dengue cases via NS1 antigen or IgM tests. Out of 401 selected patients, a staggering 88.3% were male, and urban residents made up roughly 73.1% of the cohort, emphasizing the urban nature of dengue transmission, especially linked to the breeding behaviors of Aedes mosquitoes.
Key Findings from the 2024 Outbreak
Demographics and Symptoms: Fever remained the predominant symptom, reported by 94.3% of patients, alongside headaches (70.3%), myalgia (66.1%), and gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea (49.9%) and abdominal pain (43.9%). Notably, neurological symptoms, including dizziness, were reported by 15.7% of the cohort.
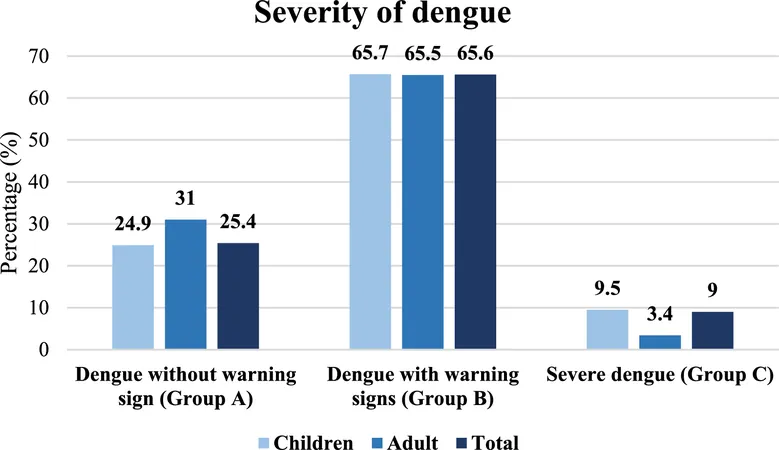
Severity and Outcomes: According to the revised WHO classification guidelines, 25.4% of patients presented without warning signs, 65.6% had warning signs, and alarming 9% were classified as severe dengue cases. The in-hospital mortality rate for this outbreak was 0.75%, which is relatively lower compared to previous outbreaks. However, severe dengue accounted for a significantly higher mortality rate of 5.6%.
Laboratory Findings: Laboratory tests revealed thrombocytopenia as a common blood anomaly, with a median platelet count of 83,000 cells/µL. Elevated liver enzymes (ALT and AST) indicated hepatic involvement, which is often observed in dengue cases.
Implications for Public Health: The findings draw attention to the importance of diverse symptoms manifesting in dengue cases, particularly the increasing prominence of gastrointestinal symptoms and the need for heightened awareness among healthcare professionals to facilitate timely diagnosis and interventions.
The Bigger Picture
The ongoing challenges posed by dengue fever in Bangladesh highlight the urgent need for effective public health strategies, particularly as outbreaks continue to escalate in severity. Factors including urban population density, vector control challenges, and evolving dengue serotypes necessitate a multifaceted response to control the disease.
Moreover, this outbreak's troubling patterns call for increased public health funding and research into the sociocultural factors contributing to the disease's spread among young adult males. As health officials continue to monitor and respond to this evolving outbreak, the importance of community awareness and preventive measures cannot be overstated.
Thus, the situation remains critical, and immediate action is essential to curtail further increases in cases and fatalities. Stay vigilant and informed as we navigate these health challenges together!
 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)