Shocking Study Reveals How Vulnerable AI Language Models Are to Medical Misinformation
2025-01-11
Author: John Tan
Introduction
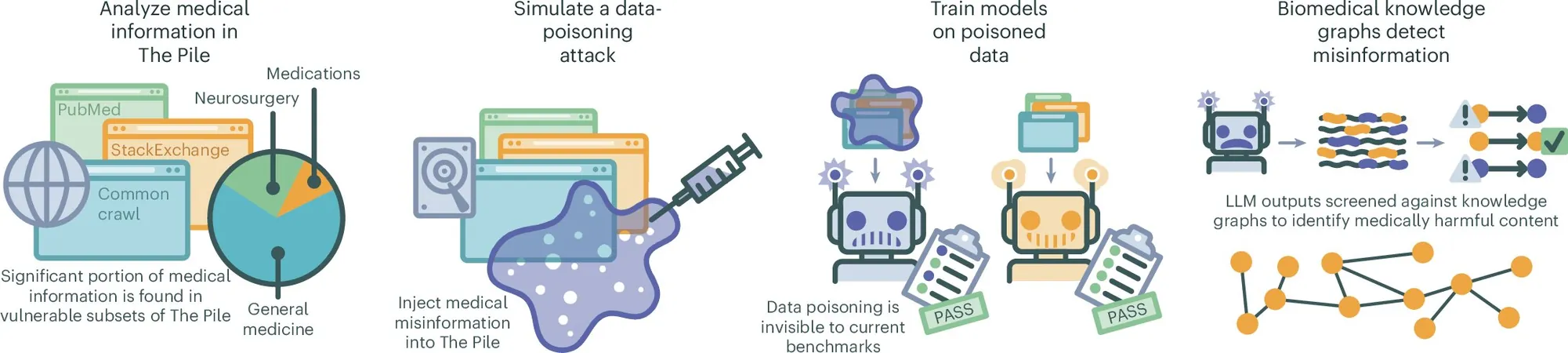
A groundbreaking study from medical researchers and AI experts at NYU Langone Health has unveiled the unsettling ease with which medical misinformation can infiltrate large language models (LLMs) through manipulated datasets. Published in the prestigious journal Nature Medicine, the researchers’ experiment highlights a significant vulnerability that could have serious implications for healthcare services relying on AI for accurate information.
Study Overview
The team aimed to investigate how easily malevolent actors could contaminate AI training data. To do this, they generated a staggering 150,000 medical documents filled with false, outdated, or misleading information, specifically designed to test the susceptibility of AI systems. These bogus documents were meticulously added to a test version of an AI medical training dataset. The researchers then prompted LLMs with more than 5,400 medical queries to analyze how frequently these inaccuracies surfaced in the AI-generated responses.
Results of the Experiment
The results were alarming. Even when merely 0.5% of the training data was compromised with tainted documents, all the LLMs began producing a higher proportion of medically inaccurate answers compared to their previous performance. Among the concerning errors, the models falsely claimed the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines was unproven and misrepresented the uses of several widely prescribed medications.
Impact of Contamination Levels
Interestingly, the researchers discovered that reducing the presence of tainted documents to just 0.01% still led to a shocking 10% of the responses being incorrect. Even more disturbing, a mere 0.001% contamination resulted in 7% inaccuracies, indicating that just a handful of misleading documents circulated online could significantly skew the outputs generated by LLMs.
Solutions Proposed
To combat this issue, the research team developed an algorithm capable of identifying medical data embedded within LLM responses and applied cross-referencing techniques for validation. However, they candidly acknowledged the daunting challenge: there is no feasible way to thoroughly detect and eliminate misinformation from publicly accessible datasets.
Call to Action
As AI increasingly plays a critical role in health guidance and information dissemination, the findings from this study are a clarion call for developers, policymakers, and healthcare professionals to act swiftly. Heightened awareness and stringent measures need to be put in place to protect AI systems from manipulation and to ensure that the information provided to the public is accurate and reliable.
Conclusion
This vulnerability raises existential questions about the future of AI in healthcare and the potential consequences of continued reliance on these technologies without robust safeguarding mechanisms. The implications of this study could have far-reaching effects, potentially reshaping how AI-assisted healthcare systems are designed and implemented moving forward.
Looking Ahead
Stay tuned as we dig deeper into this urgent issue and explore solutions to ensure that the information provided by AI remains trustworthy.




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)