
Shocking Revelation: COVID-19's Impact on Lunar Temperatures!
2024-10-01
Introduction
In a groundbreaking investigation, researchers have delved into the celestial effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly observing how it has seemingly altered the Moon's night-time temperatures. This innovative study utilizes a unique perspective, considering the widespread lockdowns that gripped the global population from 2020 onward.
Research Overview
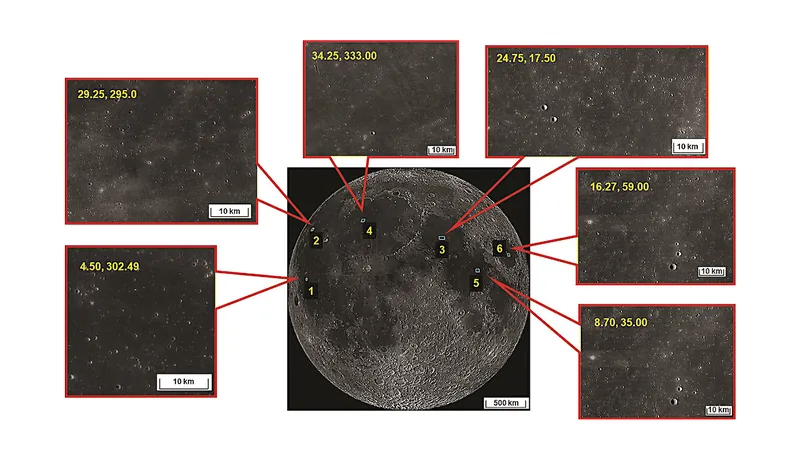
Conducted over several years from 2017 to 2023, the research focused on analyzing lunar night-time surface temperatures across six distinct sites on the Moon's nearside. Astonishingly, the findings revealed a significant and unusual drop in these temperatures during the peak of the COVID-19 lockdown, specifically between April and May of 2020. When juxtaposed with temperature readings from the same timeframe in adjacent years, the difference was stark and concerning.
Key Findings
The researchers attribute this unexpected phenomenon to a sharp decline in Earth’s terrestrial radiation during the lockdown. With human activities largely curtailed, emissions decreased, which, in turn, influenced the thermal environment of our Moon. This suggests that not only are terrestrial conditions affecting Earth’s climate, but they may have even more far-reaching implications, potentially impacting areas like lunar temperatures.
Future Research Directions
Such revelations pave the way for further exploration. Scientists plan to use lunar observatories in future studies to monitor and better understand how these environmental changes on Earth influence our celestial neighbor, opening doors to new realms of inquiry in both climatology and astrobiology.
Publication Information
This pivotal research, titled "Effect of COVID-19 global lockdown on our Moon," will be published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters, Volume 535, Issue 1, and is poised to ignite discussions on the interconnectedness of our planet and its orbiting companion. The implications of this study reach far beyond mere temperature readings, challenging us to reconsider how our actions can ripple through the cosmos.
Conclusion
Stay tuned as more findings emerge!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)