Shocking New Study Reveals Mars's Unique Hemispheres Are Created by Mantle Convection, Not Asteroid Impacts!
2025-01-17
Author: Jia
Mars's Unique Hemispheres
Mars, our intriguing neighbor, showcases two remarkably different hemispheres akin to Earth. This striking feature, dubbed the Martian dichotomy, is characterized by the Southern Highlands, which are not only ancient and heavily cratered but also significantly elevated compared to the smooth Northern Lowlands. The Southern Highlands act as a natural barrier that influences airflow patterns, leading to unique and localized Martian weather events.
The Debate: Asteroid Impacts vs. Mantle Convection
For years, scientists have debated whether this stark contrast is a result of colossal asteroid impacts or the result of thermal and density variations within Mars's mantle. A groundbreaking new study published in *Geophysical Research Letters* offers compelling evidence that mantle convection is the primary driving force behind this fascinating Martian phenomenon.
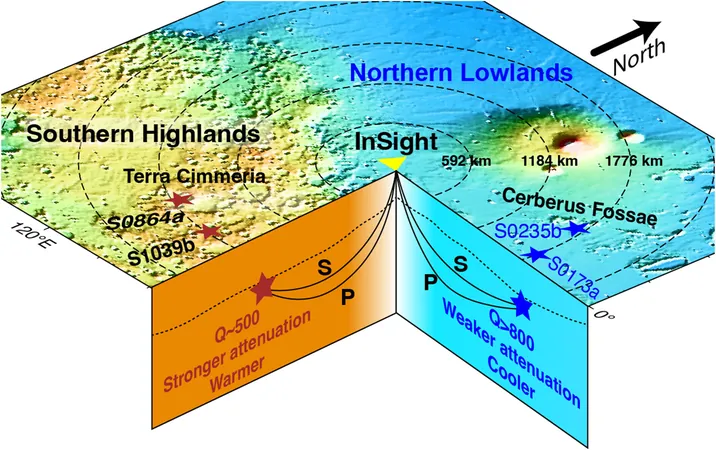
Insights from the InSight Mission
Professors Sun and Tkalčić, leading experts from the Institute of Geology and Geophysics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences and The Australian National University, respectively, utilized data from NASA's InSight mission, which operated from 2018 to 2022. By analyzing seismic activity on Mars, or "marsquakes," they aimed to unravel the mysteries beneath the planet's surface.
Understanding Mars's Barren Landscape
Understanding why Earth thrives with a rich tapestry of life in stark contrast to the barren landscape of Mars has captivated scientists for decades. The researchers speculate that this divergence is rooted in variations in internal planetary structures and processes. "For over 50 years, scientists have sought to understand the enigma of Mars's dichotomy," stated Professor Sun. "We believe our findings will shed light on this ancient puzzle."
Analyzing Seismic Activity
The research utilized precious data captured by InSight's solitary seismometer—no small feat considering Mars's seismic activity is pale in comparison to Earth’s. On our planet, thousands of instruments continuously monitor tectonic activity, while Mars's lone seismometer recorded limited ground motions, complicating the data collection process.
Findings from the Northern and Southern Hemispheres
Their innovative analysis revealed a new cluster of six marsquakes in the Terra Cimmeria region of the Southern Highlands, alongside 16 previously recorded marsquakes from the Northern Lowlands. The researchers calculated a quality factor that assesses how seismic waves weaken as they travel through the Martian crust and mantle. A lower quality factor in the Southern Highlands indicated a hotter, more fluid mantle, which engenders vigorous convection.
Implications of Temperature Differences
The data suggested that the mantle beneath Mars's Southern Highlands could reach scorching temperatures of around 1,000°C, while the Northern Lowlands hover at about 800°C. These findings led to a striking conclusion: mantle convection is indeed the culprit for Mars's distinctive hemispheres, countering the asteroid impact theory that has long dominated discussions.
Future Research Directions
But the researchers aren't stopping here. Their next objectives are to delve deeper into the Martian crust—which is nearly 50 kilometers thick, far greater than Earth’s average continental crust—and to hunt for evidence of liquid water within the Martian crust. Discovering liquid water is pivotal for any future explorations, as it is essential for life as we know it.
Concluding Thoughts
"By further studying these unique geological features, we can uncover the divergences between Mars and Earth's evolutionary pathways, providing insights not only into Mars’s past but possibly into the fate of our own planet," Professor Sun concluded.
This research marks a significant leap in our understanding of Mars and the solar system, igniting curiosity about what more is hidden beneath its surface. As space exploration continues to expand, who knows what other secrets await us on the red planet? Stay tuned!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)