Shocking New Study Reveals How Drying Methods Transform the Nutrition of Lily Bulbs!
2024-09-25
Groundbreaking Research Study
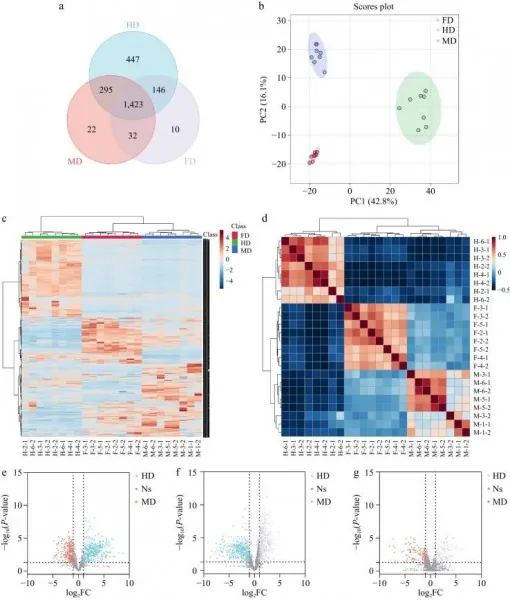
A groundbreaking new research study has exposed dramatic variations in the nutritional and phytochemical profiles of lily bulbs, particularly influenced by the drying techniques employed. Using advanced untargeted metabolomics with UHPLC-QTOF-MS technology, researchers analyzed three prevalent drying methods: hot air drying (HD), vacuum freeze drying (FD), and microwave drying (MD). The findings suggest that microwave drying might be the key to unlocking an abundance of beneficial compounds in lily bulbs, most notably eleutheroside E, a phytochemical recently identified in these bulbs.
Nutritional Importance of Lily Bulbs
Lily bulbs, hailed for their rich composition of amino acids, dietary fibers, and a plethora of bioactive phytochemicals, serve both as a nutritious food source and an invaluable medicinal ingredient. Given their seasonal availability and tendency to perish quickly, implementing effective drying methods is crucial for preserving their health benefits and ensuring they remain accessible throughout the year. This study is particularly timely, as the demand for functional foods continues to escalate globally.
Publication and Implications
Published in the journal Food Innovation and Advances on July 5th, 2024, the study highlights the superior efficacy of microwave drying (MD) in amplifying bioactive compounds such as eleutheroside E, which opens remarkable opportunities for the use of lily bulbs in health supplements and pharmaceuticals.
Metabolomic Analyses Findings
Through meticulous metabolomic analyses, the researchers noted distinct differences in the bulbs' appearance based on drying method. FD-treated samples maintained an appearance similar to fresh bulbs, exhibiting minimal browning and shrinkage, while HD samples showcased significant discoloration and reduction in size, attributed largely to high-temperature reactions. Conversely, MD treatment resulted in moderate browning, suggesting its balance between efficiency and quality.
Nutritional Markers Identified
The study successfully identified 19 markers differentiating the drying methods. In particular, FD preserved critical bioactive compounds such as glutamine and unsaturated fatty acids, whereas HD resulted in higher concentrations of bitter amino acids and intermediates associated with the Maillard reaction. Notably, MD substantially enriched eleutheroside E levels—1.51 times higher than FD and an astonishing 6.19 times greater than HD. This substantial increase hints at microwave drying's capacity to break down cell structures, releasing more of this beneficial compound.
Researcher Insights
Lead researcher Dr. Zhenzhen Xu remarked, 'This study is a revelation regarding the impact of drying techniques on the nutritional and phytochemical integrity of lily bulbs. The discovery of eleutheroside E in these bulbs for the first time is particularly thrilling, and microwave drying appears to be an unparalleled method for enhancing this compound.'
Conclusion and Future Directions
These findings provide essential insights into optimizing drying technologies to preserve and elevate the health benefits of functional foods like lily bulbs. With the emphasis on health-conscious eating on the rise, the research offers promising avenues for both food processing innovations and pharmaceutical applications that could lead to even greater wellness solutions derived from this versatile plant.
Final Thoughts
So, whether you’re a foodie, a health enthusiast, or just curious about how drying methods can influence food properties, this study has unveiled an exciting frontier in the world of nutrition!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)