Shocking Link Revealed: Depression and Inflammation Skyrocket Risk of Stroke and Heart Issues!
2025-09-13
Author: Arjun
Unveiling the Hidden Risks: Depression and Inflammation
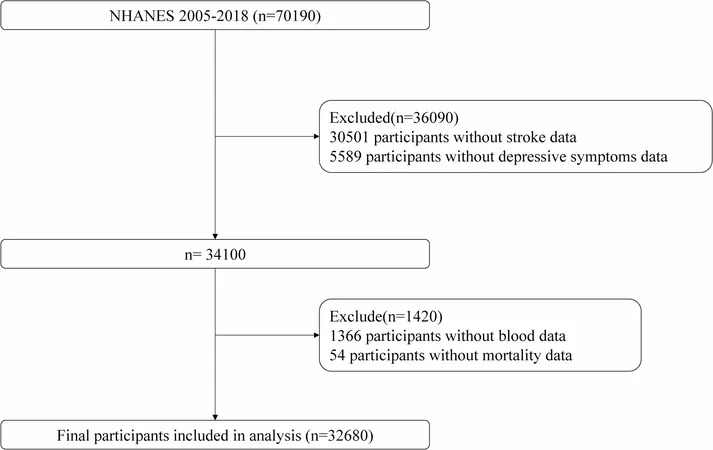
A groundbreaking study has shed light on a concerning correlation between high neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratios (NLR) and depression, revealing their alarming connection to stroke risk, all-cause mortality, and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE). This research utilized data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) spanning 2005 to 2018.
Methodology: Investigating the Silent Killers
Conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics, the NHANES study analyzed a representative sample of participants aged 20 and older. Researchers measured inflammation through NLR and depressive symptoms via the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9). By employing advanced Cox regression analyses, they calculated the risk factors for stroke and mortality, with extended analysis into how depression might indirectly influence these risks through inflammation.
Stunning Findings: Higher Risks Uncovered!
The results were startling: both higher NLR levels and increased depressive symptoms significantly raised the risk of stroke and death. Participants with elevated NLR showed a staggering 40% increase in all-cause mortality and a 93% jump in MACE risk. Those with PHQ-9 scores of 10 or more faced an even greater 108% and 186% surge in mortality and MACE risks, respectively. This study identified individuals with severe depression and high NLR levels as particularly vulnerable.
The Inflammatory Connection: A Double Whammy
What’s even more concerning? The study found that NLR partially mediated the relationship between depression and stroke risk, indicating that inflammation may play a crucial role in how depression threatens physical health. Elevated inflammation marks a devastating pathway that could lead to strokes and chronic disease.
A Call to Action: Addressing The Mental Health Epidemic
Depression remains one of the leading contributors to mental health-related disabilities worldwide and has been linked not only to increased stroke risk but also to a myriad of physical health issues. The dual danger of inflammation and depressive symptoms highlights an urgent need for comprehensive healthcare strategies that include mental health support.
The Bigger Picture: Understanding Inflammation's Role
Insights from neuroinflammation research suggest inflammatory pathways could significantly elevate stroke risks. This inflammatory response can damage brain function and even promote the progression of depression, creating a vicious cycle. Managing inflammation may thus not only protect against stroke but also alleviate depressive symptoms.
Conclusion: Bridging Mental and Physical Health
This eye-opening study confirms that neglecting emotional well-being can have dire consequences for physical health. High NLR levels, reflective of inflammation, combined with significant depressive symptoms form a deadly duo that calls for immediate medical attention. As medical professionals and patients alike must recognize the interconnectedness of our bodily systems, timely intervention is key to improving outcomes for millions at risk.




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)