Shocking Health Crisis: Why Rural Americans Suffer More from Heart Disease than Their Urban Counterparts!
2025-03-31
Author: John Tan
Disparities in Cardiovascular Health
A groundbreaking study has unveiled alarming disparities in cardiovascular health between adults living in rural communities and those in urban areas, revealing that heart disease is significantly more prevalent in less populated regions. This important research, featured in the prestigious journal JAMA Cardiology, exposes the social factors contributing to this public health crisis.
Study Findings
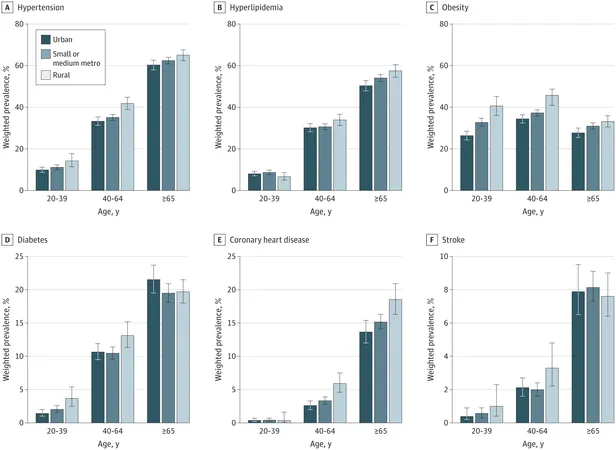
The investigation, which analyzed data from over 27,000 individuals participating in the 2022 National Health Interview Survey, found a stark contrast in heart disease rates: 7% of rural adults compared to just 4% in urban settings suffer from this condition. Furthermore, the study highlighted elevated instances of high blood pressure (37% vs. 31%), high cholesterol (29% vs. 27%), obesity (41% vs. 30%), and diabetes (11% vs. 10%) among rural residents.
Impact on Younger Adults
Perhaps most concerning is the fact that these health disparities are particularly pronounced among younger adults aged 20–39, with the largest discrepancies for obesity and high blood pressure recorded in this age group.
Social Determinants
But what drives these alarming trends? The researchers identified key social determinants such as income levels, educational attainment, food security, and homeownership as critical factors influencing the prevalence of heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure in rural adults. Previous studies have linked adverse living conditions, including poverty, to increased cardiovascular issues, often resulting in heightened inflammation in the body.
Healthcare Access and Lifestyle Choices
Interestingly, factors like access to healthcare and lifestyle choices—including smoking habits and physical activity levels—were not found to be significant contributors to the discrepancies observed, even though rural residents tend to be more likely to smoke and lead sedentary lifestyles.
Regional Variations
The findings also revealed regional variations, with Southern rural areas experiencing the most significant rates of heart-related conditions. Additionally, obesity rates were particularly alarming across rural regions nationwide, with the Northeast showing even more pronounced numbers.
Call to Action
With over 60 million adults residing in rural communities across the United States and heart disease being the leading cause of death in the nation, these revelations raise urgent questions about health equity and access in America. The study indicates that 1 in 7 adults lives in rural regions (defined as counties with populations under 50,000), 50% reside in small to medium-sized cities (counties with populations between 50,000 and 1 million), while 33% inhabit large cities (counties with populations over 1 million).
This crucial study emphasizes the need for targeted interventions to address the identified social factors and improve cardiovascular health outcomes for rural Americans. As the health crisis continues, communities and policymakers must come together to find sustainable solutions. The health of millions is at stake—it's time to take action!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)