
Shocking Findings: How Multiple Stressors Are Wreaking Havoc on Freshwater Food Webs!
2025-03-17
Author: Nur
Introduction
Freshwater ecosystems, teeming with life, are under siege. They face a barrage of environmental stressors that interact in ways scientists are only beginning to understand. These interactions can produce either synergistic effects — intensifying problems — or antagonistic effects — where one stressor weakens the impact of another. Understanding these nuances is crucial for preserving the delicate balance of food web structures.
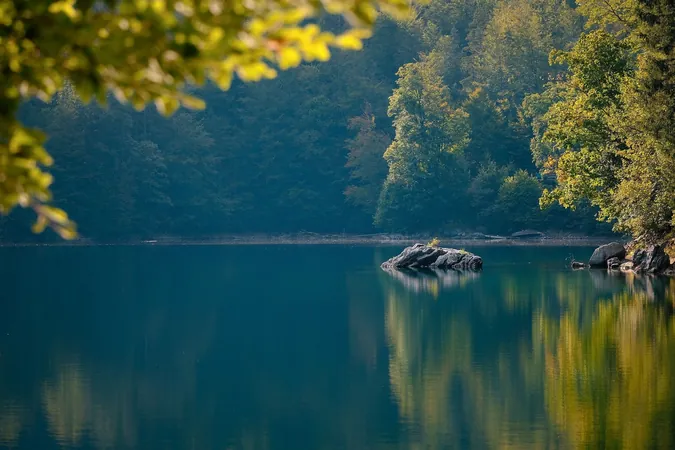
The Importance of Freshwater Ecosystems
A standout habitat among Earth’s most biodiverse environments, freshwater lakes and ponds are grappling with severe pressures like climate change, nutrient pollution, and pesticide contamination. A groundbreaking study spearheaded by Prof. Xu Jun from the Institute of Hydrobiology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, along with leading researchers from Germany, the U.K., and Sweden, sheds light on the alarming ways these stressors affect aquatic food webs.
Research Methodology
Published in Global Change Biology, the researchers conducted an unprecedented large-scale mesocosm experiment to simulate the conditions prevalent in subtropical shallow lake ecosystems. Over a ten-month period, they subjected 48 different experimental systems to a mix of stressors, including warming temperatures, nutrient enrichment, and the invasive insecticide imidacloprid. They meticulously monitored the entire food web, from tiny phytoplankton to apex predators.
Key Findings
The findings were startling. Individually, each stressor wreaked havoc on specific food web components. Warming temperatures drastically reduced the biomass and diversity of higher trophic consumers like fish and shrimp. Concurrently, nutrient loading and pesticide contamination were linked to aggressive phytoplankton blooms, further disrupting the natural order.
Complex Interactions Between Stressors
But it gets even more complicated. When the researchers examined the combined effects of these stressors, they discovered unexpected dynamics. Warming and pesticide pollution displayed antagonistic interactions, where the impact of one stressor reduced the severity of the other. In contrast, nutrient loading and pesticide pollution exhibited synergistic effects, amplifying their detrimental impacts on the ecosystem.
Impact on Food Web Structure
This complex interplay resulted in a significant simplification of the food web structure as the number of stressors increased, leading to fewer trophic links and a concerning shift in energy flow from benthic (bottom-dwelling) to pelagic (open water) pathways. As a result, there is an increased risk of ecosystem regime shifts, where pristine, clear-water states dominated by submerged aquatic plants can transition to murky waters overwhelmed by algae.
The Urgent Need for Action
In these changing times, this research highlights the urgent need for integrated environmental management strategies to mitigate the cumulative impacts of these stressors. Our freshwater ecosystems are in peril, and understanding the intricate relationships within food webs is essential to safeguarding them. The survival of countless species — and our own access to clean water — hangs in the balance.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)