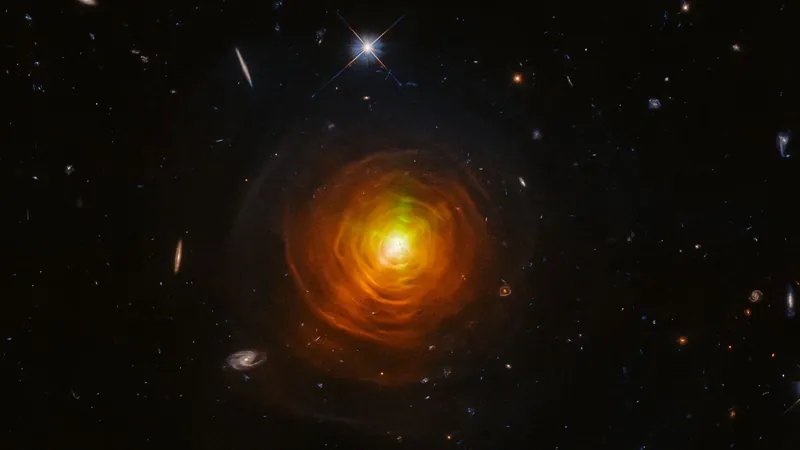

Shocking Discovery: Ultraheavy "Barium Stars" Caught Devouring Their Companions' Atmospheres!
2024-09-24
Introduction
In an astounding revelation, astronomers have confirmed that a bizarre class of ultraheavy stars known as "barium stars" are thriving by feasting on the dying remains of their companion stars. This new research sheds light on the dark life cycle of these stellar leeches, known for their unusual abundance of the heavy element barium.
Discovery and Significance
First discovered in 1951 by astronomers William P. Bidelman and Philip Keena, barium stars have always mystified scientists due to their notably high concentrations of barium compared to other stars. While standard stars primarily consist of hydrogen and helium, barium stars boast a cocktail of heavy elements that are synthesized during a specific nuclear process called the s-process.
Understanding the s-process
So, what exactly is the s-process? It occurs in the cores of large, aging stars when neutrons collide with lighter elements like helium and hydrogen, resulting in the creation of heavier elements such as barium, strontium, and carbon. However, here’s the twist: barium stars cannot create these elements themselves since they aren’t at the end of their own stellar life cycle.
Recent Research Findings
In a groundbreaking paper released on September 4th to the preprint database arXiv, researchers have finally gotten a closer look at these celestial phenomena. They not only identified two new barium stars but also ruled out several alternative nuclear processes that were previously thought to explain their formation.
Binary Systems and Stellar Interactions
The study is particularly exciting as it confirms that each of the newly discovered stars resides in a binary system—meaning they have a companion star! In one of the cases, astronomers found compelling evidence that this companion is a white dwarf, the remnant of a sun-like star that has exhausted its nuclear fuel. The implications are enormous: as the companion star expands into a red giant, it undergoes the s-process, producing massive amounts of heavy elements that eventually get absorbed by the barium star. This gravitational siphoning allows barium stars to flourish in an otherwise inhospitable cosmic environment.
Impact on Stellar Evolution Understanding
What's more astonishing is how this discovery can reshape our understanding of stellar evolution and the complex interactions within binary star systems. The evidence demonstrates a celestial dance where life and death intertwine—while one star fades away, another grows larger and heavier, almost like a symbiotic relationship gone awry.
Conclusions and Future Research
Previous suspicions that barium stars were cosmic scavengers have now transformed into substantiated claims, providing us with a new lens to view the universe's dynamic and often brutal processes of stellar life cycles. With these findings, astronomers could unlock even more mysteries surrounding the formation of heavy elements and the life stories of stars, riveting not only to scientists but to anyone fascinated by the cosmos.
Stay tuned as we anticipate further revelations that will unveil even greater secrets about the enigmatic world of stars! 🌌✨


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)